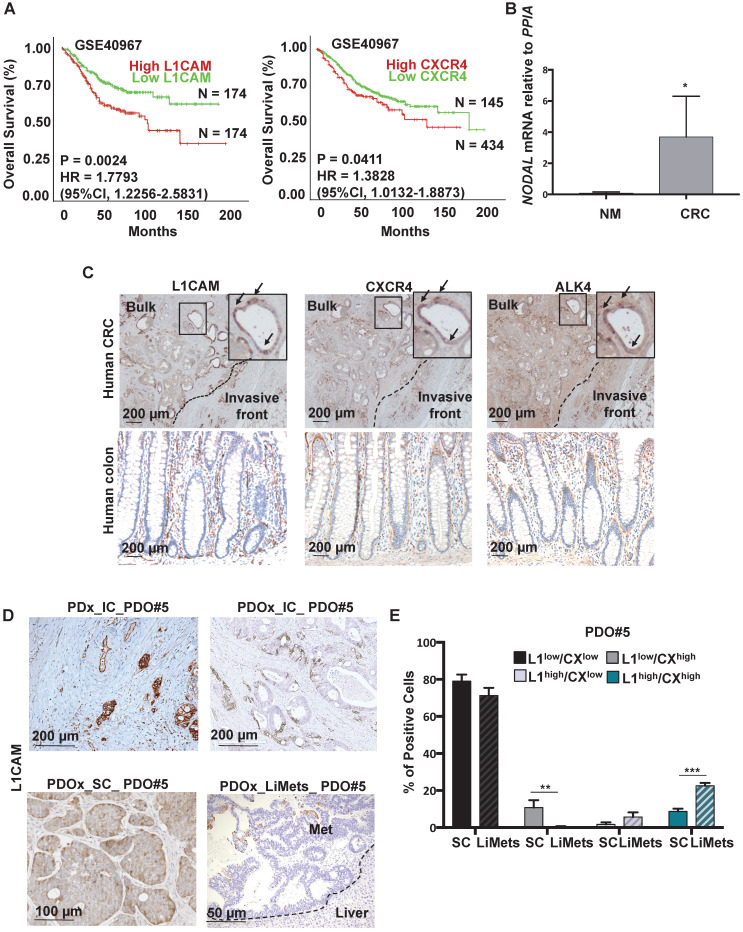
Figure 1.
Detection of L1CAM/CXCR4 subpopulation in human CRC. (A) Kaplan-Meier curves showing overall survival of CRC patients, stratified according to the median value of L1CAM (n = 348, left panel) and CXCR4 (n = 579, right panel) expression. A Median Group cut-off (50% High vs 50% Low) was used for L1CAM and (25% High vs 75% Low) was used for CXCR4. (B) qPCR analysis for NODAL in 3 Human Normal Mucosa samples and 10 Human CRC samples. Data are normalized to PPIA expression. *p<0.05. Data are mean ± SD. (C) Representative immunohistochemistry for L1CAM, CXCR4 and ALK4 (brown) in tissue sections from CRC patients (upper panel, n = 10) and normal human colon (lower panel, n = 3). (D) Representative immunohistochemistry for L1CAM (brown) of Patient-Derived-xenograft (PDx) generated from primary tumors injected in the caecum (IC) of immunocompromised mice, and their matched Patient-Derived-Organoids-xenograft injected in the caecum (PDOx_IC), subcutaneously (PDOx_SC) or their raised liver metastasis (LiMets). (E) L1CAM and CXCR4 staining % evaluated by flow cytometry in the PDOx_SC derived cells compared with the PDOx_LiMets derived cells. All cytometry gates were established based on isotype controls.**p<0.005, ***p<0.0005. Data are mean ± SD, n ≥6.