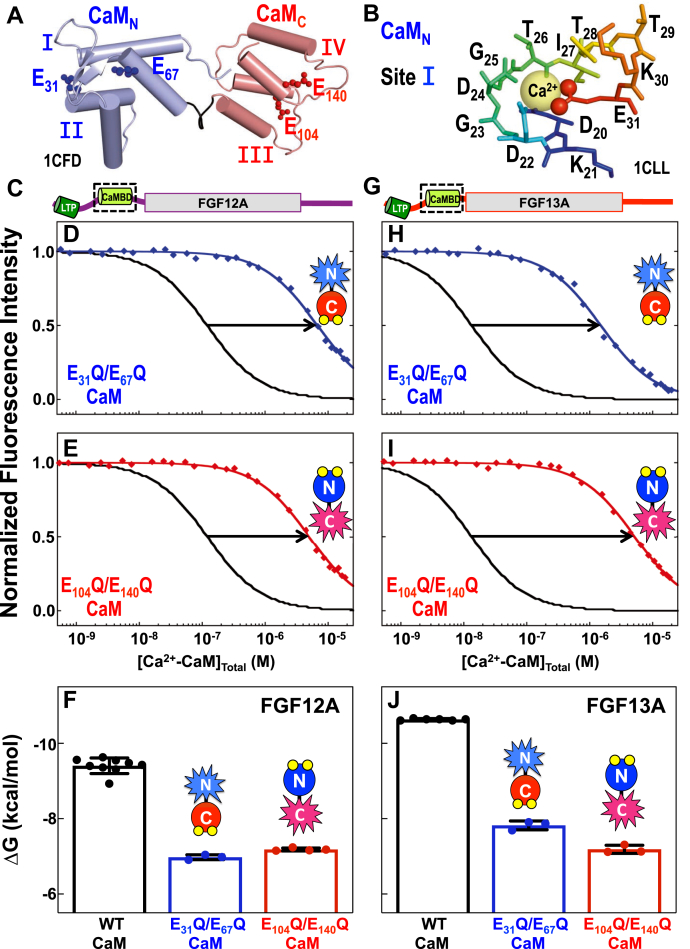
Figure 3.
Energetic contribution of CaMNand CaMCto FGF12A and FGF13A CaMBD binding by CaM.A, position of E31 (blue), E67 (blue), E104 (red), and E140 (red), shown as ball-and-stick, in apo CaM (1CFD, CaMN/light blue, CaMC/salmon). B, (Ca2+)4-CaM site I (1CLL): Ca2+ (yellow sphere) is surrounded by residues D20 (blue) to E31 (red). The coordinating O atoms of E31 are shown as red spheres. C, schematic of FGF12A. Folded β-trefoil core is shown as a rectangle, and LTP (green) and CaMBD (limon) are shown as cylinders. The black box indicates the position of the FGF12A CaMBD. D and E, equilibrium titrations of the FGF12ACaMBD biosensor with E31Q/E67Q (D, blue) or E104A/E140Q CaM (E, red). A reference titration with WT CaM is shown in black. F, ΔG of WT (black), E31Q/E67Q (blue), and E104Q/E140Q (red) CaM binding the FGF12ACaMBD biosensor. G, schematic of FGF13A. Folded β-trefoil core is shown as a rectangle, and LTP (green) and CaMBD (limon) are shown as cylinders. The black box indicates the position of the FGF13A CaMBD. H and I, equilibrium titrations of the FGF13ACaMBD biosensor with E31Q/E67Q (H, blue) or E104A/E140Q CaM (I, red). A reference titration with WT CaM is shown in black. J, ΔG of WT (black), E31Q/E67Q (blue), and E104Q/E140Q (red) CaM binding the FGF13ACaMBD biosensor.