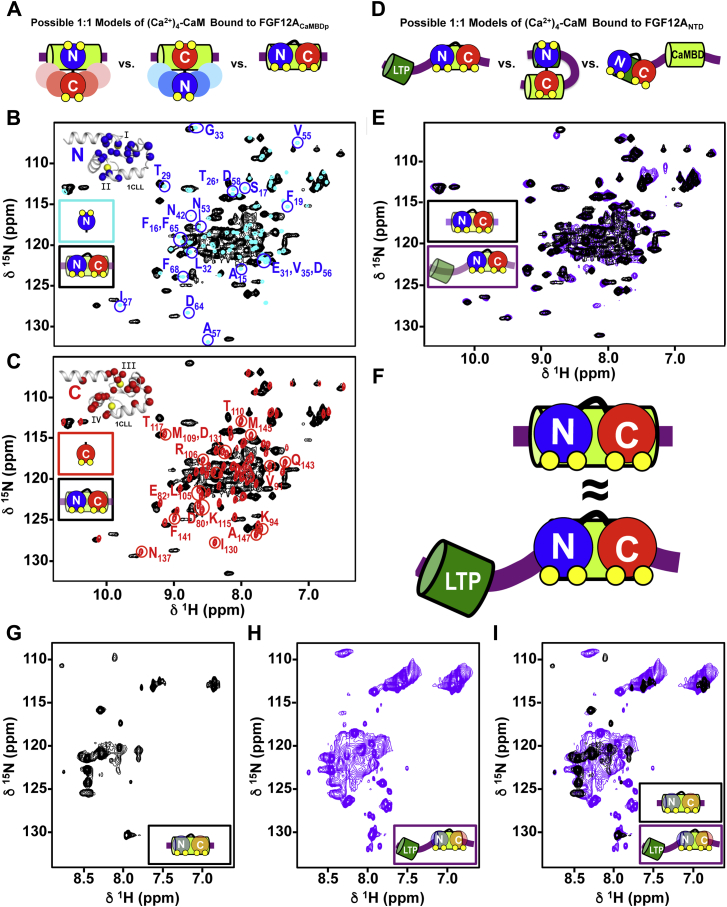
Figure 4.
Interaction of (Ca2+)4-CaM with the FGF12ACaMBDpand FGF12ANTD.A, schematics depicting models of (Ca2+)4-CaM (CaMN/blue, CaMC/red) binding to the FGF12ACaMBDp (limon cylinder) in a 1: 1 M ratio. B and C, overlay of the 15N-HSQC spectra of 15N-(Ca2+)2-CaMN (blue, B) or 15N-(Ca2+)2-CaMC (red, C) and 15N-(Ca2+)4-CaM+14N-FGF12ACaMBDp (black). Peaks labeled in the spectrum of 15N-(Ca2+)2-CaMN (B) or 15N-(Ca2+)2-CaMC (C) are shifted in the 15N-(Ca2+)4-CaM+14N-FGF12ACaMBD spectrum. Insets show the Cα of labeled CaMN (blue spheres, B) or CaMC (red spheres, C) residues on a structure of (Ca2+)4-CaM (1CLL, gray helices). D, schematics depicting models of (Ca2+)4-CaM (CaMN/blue, CaMC/red) binding to the FGF12ANTD in a 1:1 M ratio. FGF12A LTP (green) and CaMBD (limon) are shown as cylinders. E, overlay of the 15N-HSQC spectra of 15N-(Ca2+)4-CaM bound to the 14N-FGF12ACaMBDp (black) or 14N-FGF12ANTD (purple). F, schematic showing that the interface is essentially identical between (Ca2+)4-CaM (CaMN/blue, CaMC/red) and the FGF12ACaMBDp (limon cylinder) or FGF12ANTD (LTP/green cylinder, CaMBD/limon cylinder). G and H, 15N-HSQC spectrum of 14N-(Ca2+)4-CaM bound to 15N-FGF12ACaMBDp (G, black) or 15N-FGF12ANTD (H, purple). I, overlay of the 15N-HSQC spectra of 14N-(Ca2+)4-CaM bound to 15N-FGF12ACaMBDp (black) or 15N-FGF12ANTD (purple).