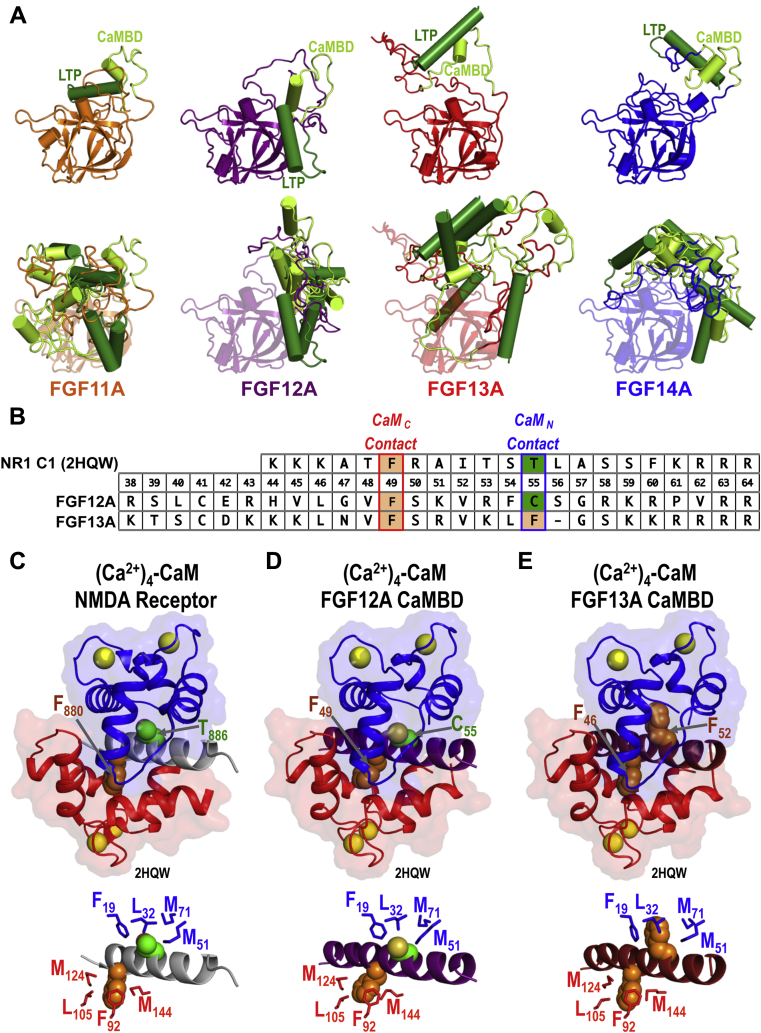
Figure 8.
Models of (Ca2+)4-CaM bound to the FGF12A and FGF13A CaMBD. In all structures CaM residues 1–75 are blue, 76–80 are black and 81–148/red, and Ca2+ are yellow spheres. A, top, model 1 in the Robetta (54) generated ensemble of each full-length A-type FGF. Bottom, orientation of the LTP and CaMBD regions in the modeled ensemble of FGF11, FGF12A, FGF13A, and FGF14. The FGF isoforms are colored as follows: FGF11A is orange, FGF12A is purple, FGF13A is red, and FGF14A is blue. The LTP and CaMBD regions of each FGF are shown in green and limon, respectively. Models were aligned with FGF12A a.a. 71–204. B, alignment of the NMDA receptor CaMBD, FGF12A CaMBD, and FGF13A CaMBD sequences. The positions that correspond to F880 and T886in the NMDA receptor are shaded (hydrophobic/tan, polar/green). C: Structure of (Ca2+)4-CaM bound to the NMDA receptor CaMBD (2HQW, gray), F880 (orange), and T886 (green) of the NMDA receptor are shown as spheres (top) and positions of F19, L32, M51, and M71 in CaMN (blue) and F92, L105, M124, and M144 in CaMC (red) are shown as sticks relative to F880 (orange spheres) and T886 (green spheres) in the NMDA receptor CaMBD (lower). D: Model of (Ca2+)4-CaM bound to the FGF12A CaMBD (purple), F49 (orange), and C55 (green) of FGF12A are shown as spheres (top) and positions of F19, L32, M51, and M71 in CaMN (blue) and F92, L105, M124, and M144 in CaMC (red) are shown as sticks relative to F49 (orange spheres) and C55 (green spheres) in the FGF12A CaMBD (bottom). E, model of (Ca2+)4-CaM bound to the FGF13A CaMBD (firebrick), F46 and F52 of FGF13A are shown as orange spheres (top) and positions of F19, L32, M51, and M71 in CaMN (blue) and F92, L105, M124, and M144 in CaMC (red) are shown as sticks relative to F46 (orange spheres) and C52 (green spheres) in the FGF13A CaMBD (bottom).