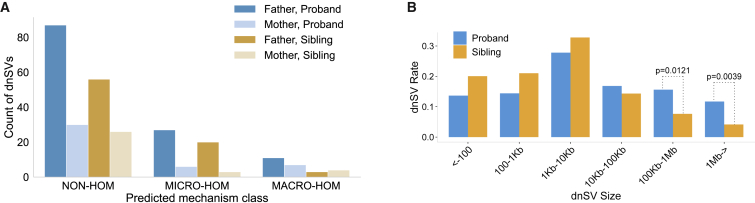
Figure 4.
A comparison of dnSV breakpoint homology and size among probands and unaffected samples
(A) Counts of phased variants grouped by predicted mechanism class, parent of origin, and affected status. Mechanism classes include those characterized by no sequence homology at breakpoints (NON-HOM), microhomology at breakpoints (MICRO-HOM), or macrohomology (matching segmental duplications) at breakpoints (MACRO-HOM).
(B) Variants binned by size and compared between probands and unaffected samples. The fraction of dnSVs assigned to each bin is statistically similar except in the largest two bins where sizes are 100 kb to 1 Mb and ≥1 Mb. The difficulty of determining the size of insertion variants, especially mobile element insertions, led to exclusion of those variants from this figure.