Figure 3.
DDB1 missense variants in lymphoblast cells result in altered DNA damage signatures and histone methylation following UV damage
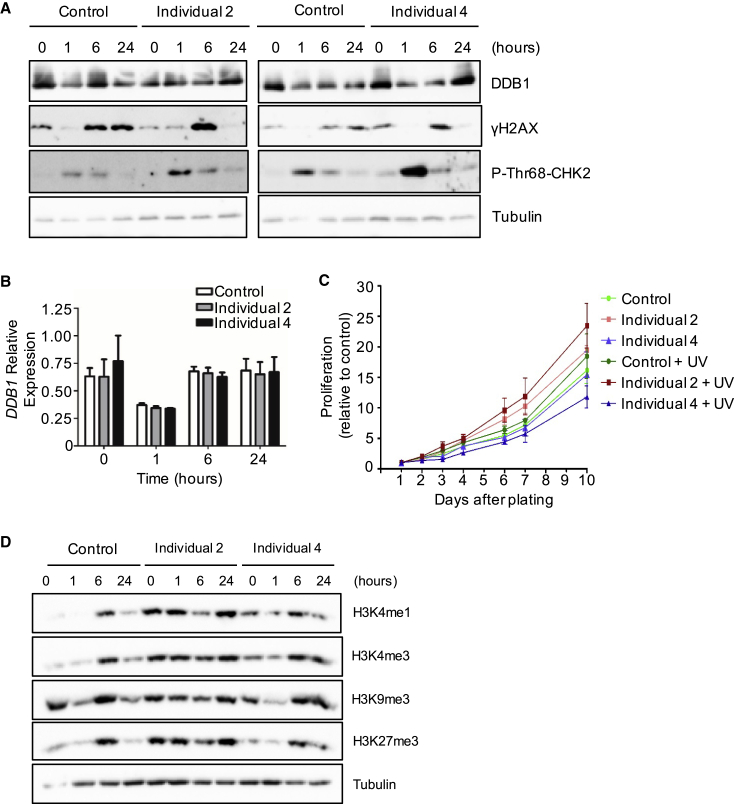
(A) Immunoblot analysis on total extracts from control and affected lymphoblast cells. Untreated cells are shown at the 0 h time point, whereas the other time intervals indicate the number of h following UV exposure. Total DDB1 and the levels of γH2AX and p-Thr68-CHK2 phosphorylation were assessed: DDB1 was found to be unchanged and γH2AX and p-Thr68-CHK2 levels were induced as expected, p-Thr68-CHK2 to a higher level than controls and γH2AX to a similar level as controls but was not sustained.
(B) Real-time PCR analysis on extracts from lymphoblast cells showing transcript levels of DDB1 before and after UV exposure are similar between cells from affected individuals and control individuals.
(C) Cell proliferation of control and affected lymphoblast cells was measured by harvesting and counting cells on each of the specified days after initial plating, either with or without UV exposure.
(D) Immunoblot analysis of total extracts from control and affected lymphoblast cells. Untreated cells are shown at the 0 h time point, whereas the other time intervals indicate the number of h following UV exposure. Levels of various histone H3 methylations were assessed and found to be abnormal in cells from affected individuals. Immunoblots in this figure are representative images of at least three biological replicates, and graphed data represent the mean of three biological replicates; error bars depict standard error of the mean.