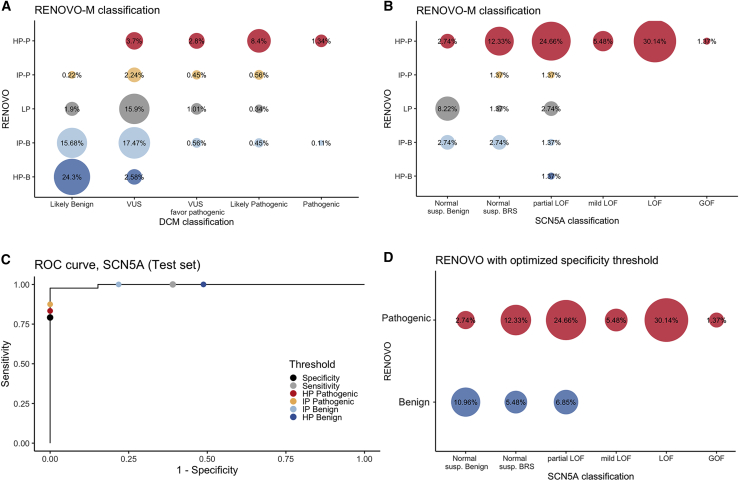
Figure 5.
RENOVO-M validation in DCM-related context
(A) Comparison of RENOVO-M and clinical-based classification of the 893 DCM variants. Bubble size represents the percentage of common variants for each RENOVO-M class and DCM class. Colors follow the classification provided by RENOVO: blue shades for HP-B and IP-B classes, red shades for HP-P and IP-P, and gray for LP.
(B) Comparison of RENOVO-M and functional classification of 73 SCN5A variants in Glazer dataset. Bubble size represents the percentage of common variants for each RENOVO-M class and SCN5A class. Color code is defined as in (A). “Normal susp. Benign” label stays for the 10 normal suspected benign variants, while “Normal susp. BRS” for the normal suspected Brugada syndrome variants.
(C) ROC curve on the test set restricted to the SCN5A gene; effects on specificity and sensitivity of diverse PLS thresholds are represented by different colors. RENOVO-M thresholds for HP-B and IP-B are colored in dark and light blue and those for HP-P and IP-P in red and orange. PLS thresholds optimized for specificity and sensitivity are represented by black and gray dots.
(D) Comparison of RENOVO-M optimized for specificity and SCN5A database. Bubble size represents the percentage of common variants for each RENOVO-M class and DCM class. Colors follow the classification provided by RENOVO: blue for benign and red for the pathogenic class.