Figure 5.
Knockout of ERF-binding sites led to elevation of HbF in HUDEP-2 and CD34+ HSPCs
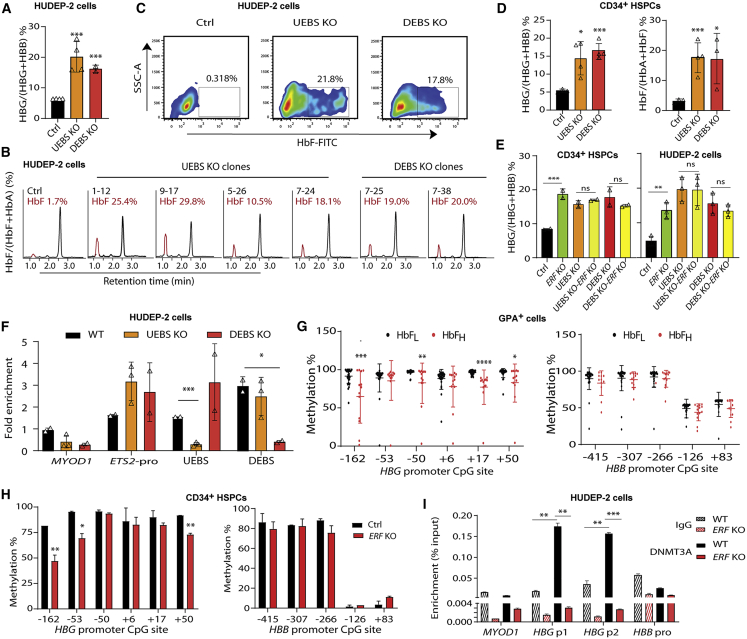
(A–C) Quantitative measurement of ERF mRNA expression by quantitative real-time PCR (A) and HbF production by HPLC (B) and by flow cytometry analysis (C) in UEBS/DEBS KO HUDEP-2 clones (n = 4 for UEBS and n = 2 for DEBS, each point indicates the mean value for each clone). The HPLC profiles of HbF from each of the six independent single UEBS/DEBS KO HUDEP-2 clones are shown.
(D) Quantitative measurement of HBG mRNA expression by quantitative real-time PCR (left) and HbF production by HPLC (right) in UEBS/DEBS KO CD34+ HSPCs (editing efficiency: 30% for UEBS, 23% for DEBS).
(E) Quantitative measurement of HBG mRNA expression by quantitative real-time PCR in single or double KO of ERF and/or UEBS (UEBS KO-ERF KO) or DEBS (DEBS KO-ERF KO) CD34+ HSPCs (left) and HUDEP-2 cells (right). The γ-globin expression levels were determined as a percentage of the total β-like globin level (HBG+HBB). One-way ANOVA was used for comparison of the indicated groups. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.01. ns, non-significant (p > 0.05).
(F) Detection of ERF-binding sites by ChIP-quantitative real-time PCR in UEBS or DEBS KO HUEDP-2 clones (n = 3 and n = 2, respectively). Data are presented as mean ± SD for each clone.
(G) Quantitative measurement of methylation levels of the HBG (left) and HBB (right) promoter by bisulfite sequencing in the independent cohort of 47 samples with β-thalassemia (HbFH: n = 13 or HbFL: n = 34).
(H) Quantitative measurement of methylation levels of the HBG promoter (left) and HBB promoter (right) by bisulfite sequencing in the ERF KO CD34+ HSPCs.
(I) ChIP-quantitative real-time PCR assay performed with DNMT3A antibody in HBG promoter in WT and ERF KO HUDEP-2 cells. HBG p1 and p2 covered the region of CpG sites from −162 to +50. MYOD1 and HBB pro served as controls.