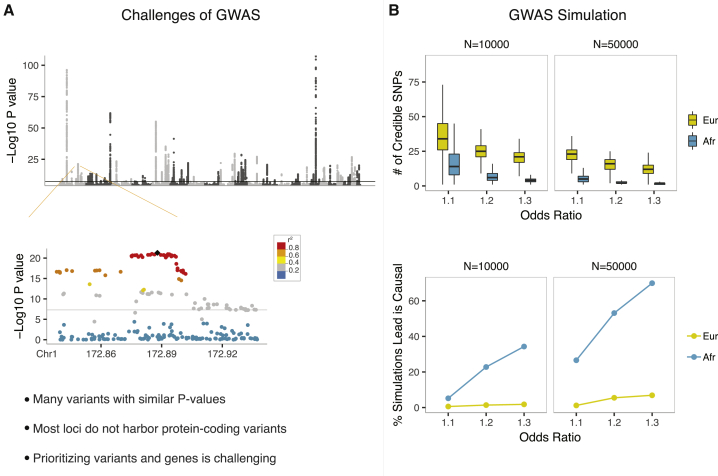
Figure 1.
Challenges of GWASs
(A) An example Manhattan plot displaying Crohn disease GWAS p values.3 The zoomed-in plot of the chr 1q24.3 locus3 illustrates the correlation between variants (r2) and association p values.
(B) The upper figure shows the number of statistically prioritized (95% credible SNP set) variants based on 1,000 simulations under different odds-ratio, sample-size, and ethnicity scenarios. The lower figure shows the percentage of simulations that identified the assigned causal variant as the lead variant. Haplotypes were constructed from 1000 Genomes European (CEU, TSI, FIN, GBR, and IBS) or African (YRI, LWK, GWD, MSL, ESN, ASW, and ACB) subjects. Common genetic variants (MAF > 0.01) across 100 kb region in the chr 1q24.3 locus shown in Figure 1A were included in haplotype construction. Among observed credible SNP set variants, a randomly chosen SNP was assigned as the causal variant for simulation purposes. GWAS p values were simulated with the simGWAS package4 under different odds-ratio, sample-size, and ethnicity scenarios. 95% credible SNP sets were calculated as implemented in the coloc package.5 Numbers of credible SNP set variants in each simulation and the percentage of simulations that identified the assigned causal SNP as the lead SNP were plotted.