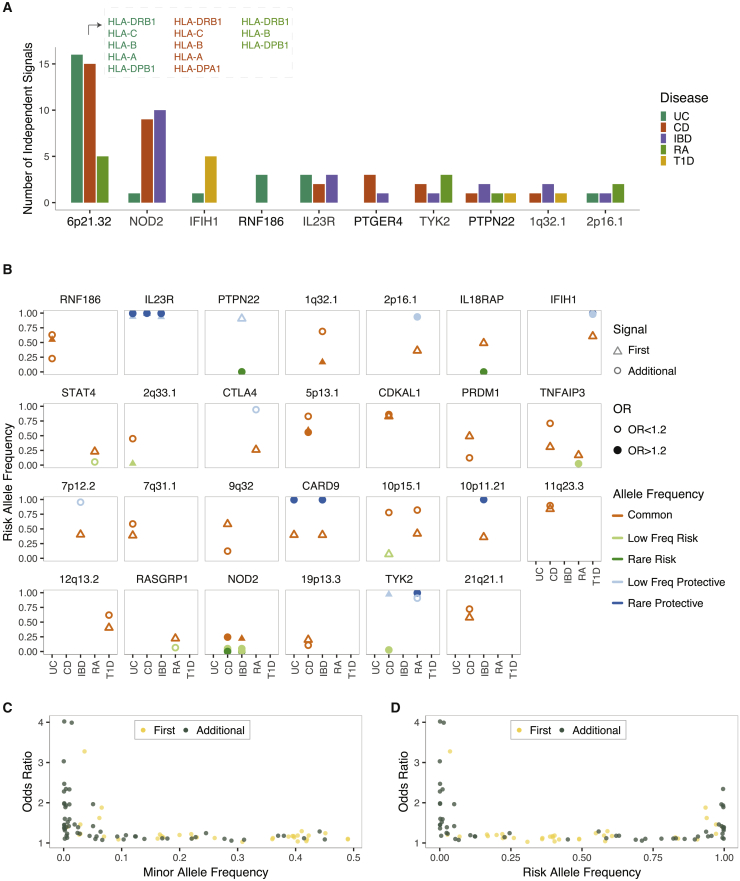
Figure 3.
The extent of allelic heterogeneity in complex autoimmune diseases
(A) Example GWAS loci where allelic heterogeneity was reported for at least one autoimmune disease.
(B) Risk-allele frequency and effect size of the first and additional signals in non-HLA loci with allelic heterogeneity. Gene names are included only when a single gene was predominantly reported as the candidate trait-relevant gene in the literature. Note that the HLA locus is not included because of the complexity of the locus and that there are inconsistencies in how genetic associations in this locus were reported (i.e, reporting was at the haplotype level, amino acid level, and nucleotide level). Common-allele frequency (AF), AF > 0.1; low-allele frequency, 0.01 < AF < 0.1; and rare-allele frequency, AF < 0.01. Abbreviations are as follows: UC, ulcerative colitis; CD, Crohn disease; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; T1D, and type 1 diabetes.
(C) The relationship between odds ratios and minor-allele frequencies.
(D) The relationship between odds ratios and risk-allele frequencies.