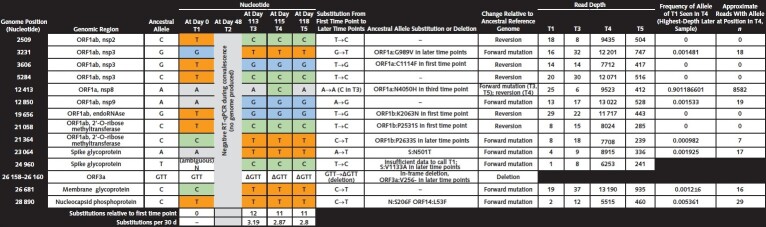
Figure 1. Genetic variation over time observed in SARS-CoV-2 genomes from patient samples.
Five nasopharyngeal specimens were collected spanning 118 d. For viral sequencing, 2 replicate sequencing libraries were prepared from source material for each sample as previously described (1). SARS-CoV-2 genomes were assembled using viral-ngs, v2.1.10.0, assembly pipelines (2). Consensus SARS-CoV-2 genomes were assembled for all positive time points, whereas no genomic data were produced from the negative RT-qPCR test result (T2). The genome from the first time point was 96.6% complete (mean depth: 18 reads), and remaining genomes were 99% complete (mean depth: tens to thousands of reads). Each assembled genome was characterized by comparison to the ancestral reference genome, NC_045512.2 (isolated from one of the first known COVID-19 cases in Wuhan, China). The 3 later time points are nearly identical and share a common set of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), with T3 having a single additional SNV. Compared with T1, these 3 genomes had more substitutions (11-12 SNVs) than expected from the mean substitution rate of SARS-CoV-2, which is approximately 1 substitution every 2 wk (3). Of note, 5 of the substitutions seen in the first time point were replaced by the ancestral allele in later time points; these apparent reversions strongly suggest that the later genomes reflect an independent infection with a virus from a distinct lineage rather than evolution of the virus of the first time point, especially given the ubiquity of SARS-CoV-2 in the surrounding community. Three amino acid changes present at the first time point were absent from the later time points, and the later time points all bear 3 new amino acid substitutions not seen in the first time point, as well as a deletion. Time points T3–T5 had a notable amino acid substitution in the receptor-binding domain of the spike glycoprotein at position 501 (S:N501T), an amino acid substitution believed to increase affinity for the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor (4). In the most deeply sequenced later time point, T4, none of the distinguishing variants of the first time point were present in high abundance, and nearly half were absent entirely. For none of the apparent reversions to the ancestral allele did a minor population exist in the most densely sequenced later time point, T4. RT-qPCR = reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction.