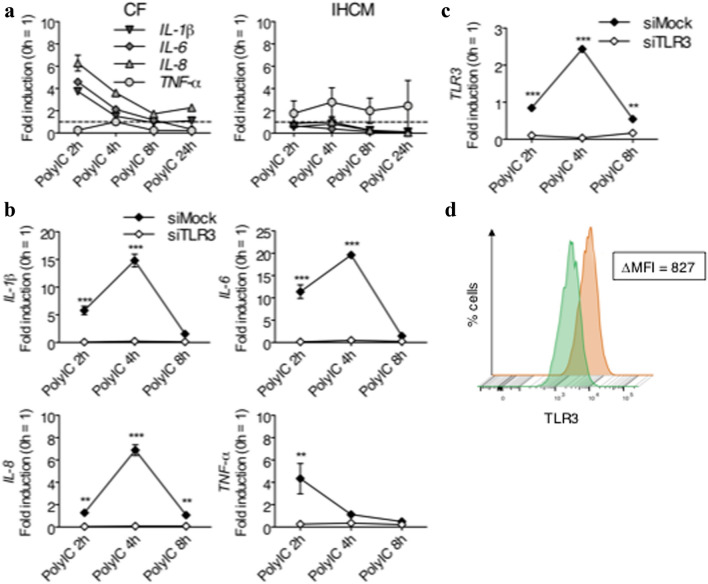
Fig. 3.
Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human CF is TLR3-dependent. (a) Human CF and IHCM were stimulated for 2, 4, 8, and 24 h with 10 ng/ml PolyIC. Transcription of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, determined by real-time RT-PCR, was positive in human CF, while in the IHCM, only TNF-α was positive. (b-c) Knockdown of TLR3 with siRNA in human CF stimulated for 2, 4, and 8 h with 10 ng/ml PolyIC. SiMock was used as a control. Real-time RT-PCR used to measure transcription of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α demonstrated that in the absence of TLR3, human CF did not express pro-inflammatory cytokines upon PolyIC stimulation (b). TLR3 knock-down efficiency was also determined by real-time RT-PCR (c). (d) Knockdown of TLR3 with siRNA in human CF stimulated for 8 h with 10 ng/ml PolyIC (green histogram). SiMock was used as a control (orange histogram). FACS analysis was performed for human CF stained with PE-conjugated anti-TLR3 antibodies. The difference between the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the human CF knocked down with siTLR3 and the MFI of the siMock control human CF was 827 MFI. Means ± s.d. and values measured form one out of two independent experiments performed in duplicates are shown. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc testing: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for siMock vs. siTLR3