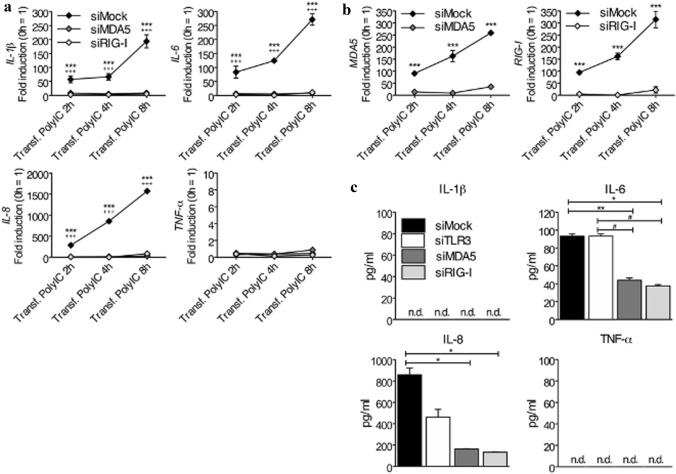
Fig. 5.
MDA5 and RIG-I regulate pro-inflammatory cytokines in human CF after intracellular PolyIC stimulation. (a-b) Knockdown of MDA5 and RIG-I with siRNA in human CF stimulated for 2, 4, and 8 h with 1 ng/ml of intracellularly transfected PolyIC. SiMock was used as a control. Transcription of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, but not of TNF-α, after stimulation with cytosolic PolyIC, was MDA5- and RIG-I-dependent (a). MDA5 and RIG-I knock-down efficiency was also determined by real-time RT-PCR (b). (c) Knockdown of TLR3, MDA5, and RIG-I with siRNA in human CF stimulated for 24 h with 1 ng/ml of intracellularly transfected PolyIC. SiMock was used as a control. IL-6 and IL-8, but not IL-1β and TNF-α, all measured at the protein level in cell-free supernatants, showed reduced levels after siRNA-induced knockdown. n.d., not detected. Means ± s.d. and values measured from one out of two to three independent experiments performed in duplicates are shown. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc testing, ***p < 0.001 for siMock vs. siMDA5, +++p < 0.001 for siMock vs. siRIG-I (a); ***p < 0.001 for siMock vs. siMDA5 (left panel) or siMock vs. siRIG-I (right panel) (b); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 for siMock vs. siMDA5 and siMock vs. siRIG-I, #p < 0.05 for siTLR3 vs. siMDA5 and siTLR3 and siRIG-I (c)