Figure 1.
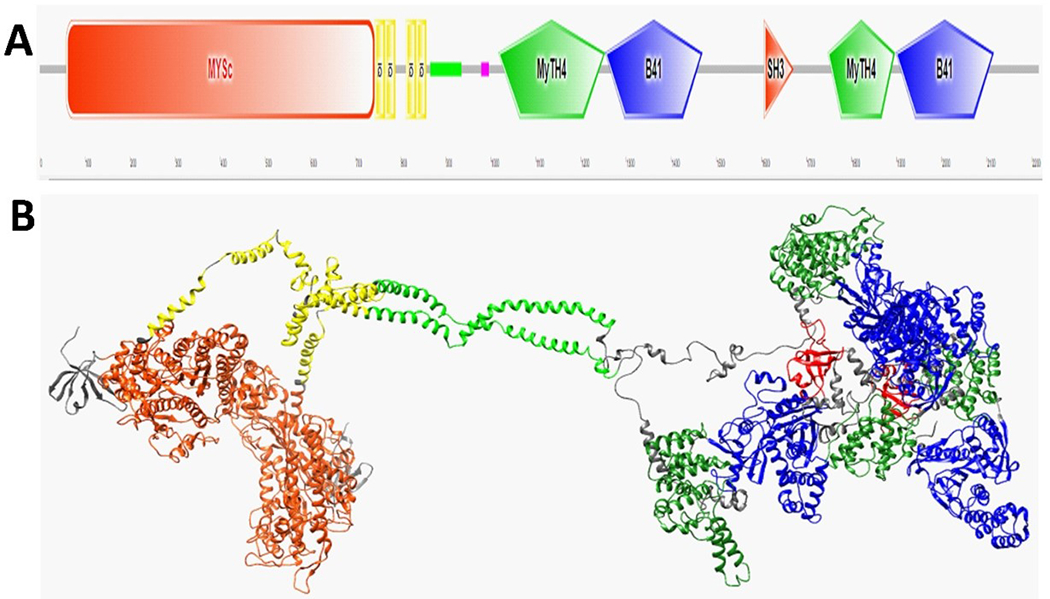
A schematic view of human MYO7A and the homology model of the human MYO7A homodimer are shown. (A) The domain structure of MYO7A predicted using SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). Motifs from left to right: motor domain (MySc, red); IQ motifs (yellow); coiled-coil region (green); low complexity area (magenta); MyTH4 domain (green); FERM1 domain (B41, blue); SH3 (orange), MyTH4 (green); and FERM2 domain (B41, blue). (B) A ribbon homology model of MYO7A homodimer is shown. Domains colored similarly to that of Panel A. Domain sizes are shown in Table 2.Also, the residues 632–639 are in the actin-binding region, residues 158–165 are involved in binding to ATP, and the residues 858–935 are in the single alpha-helix region formed by charged residues.
