Figure 1.
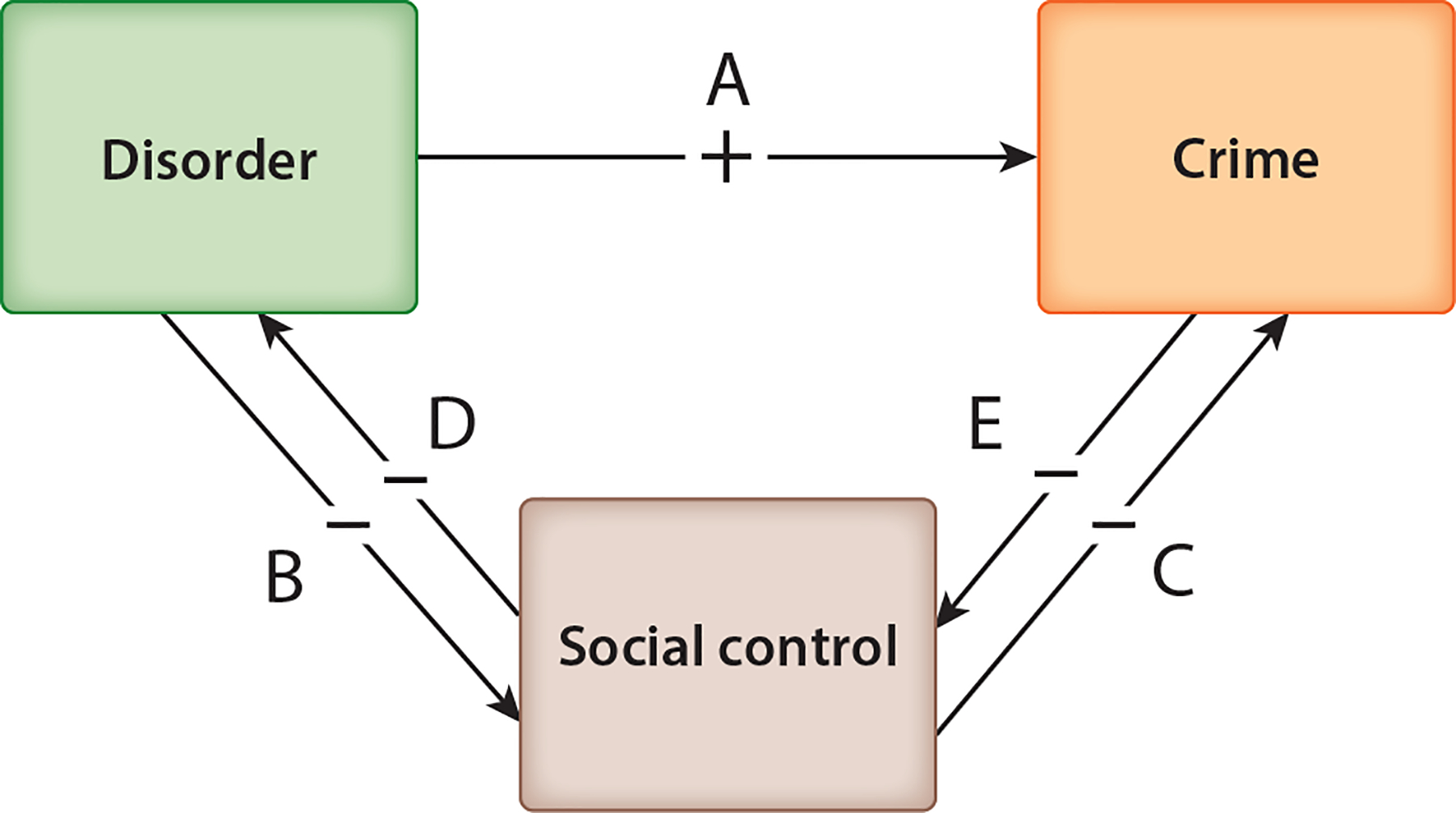
Conceptual model of broken windows theory: disorder, social control, and crime. Two paths link disorder to crime: a direct path, in which (a) disorder signals community indifference, which increases crime; and an indirect path, in which (b) disorder elicits actual community indifference, which weakens social control, which in turn (c) increases crime. These effects are reinforced as (d) weakened social control stimulates more disorder and (e) crime weakens social control. Two feedback pathways (d and e) mean this is a nonrecursive model.
