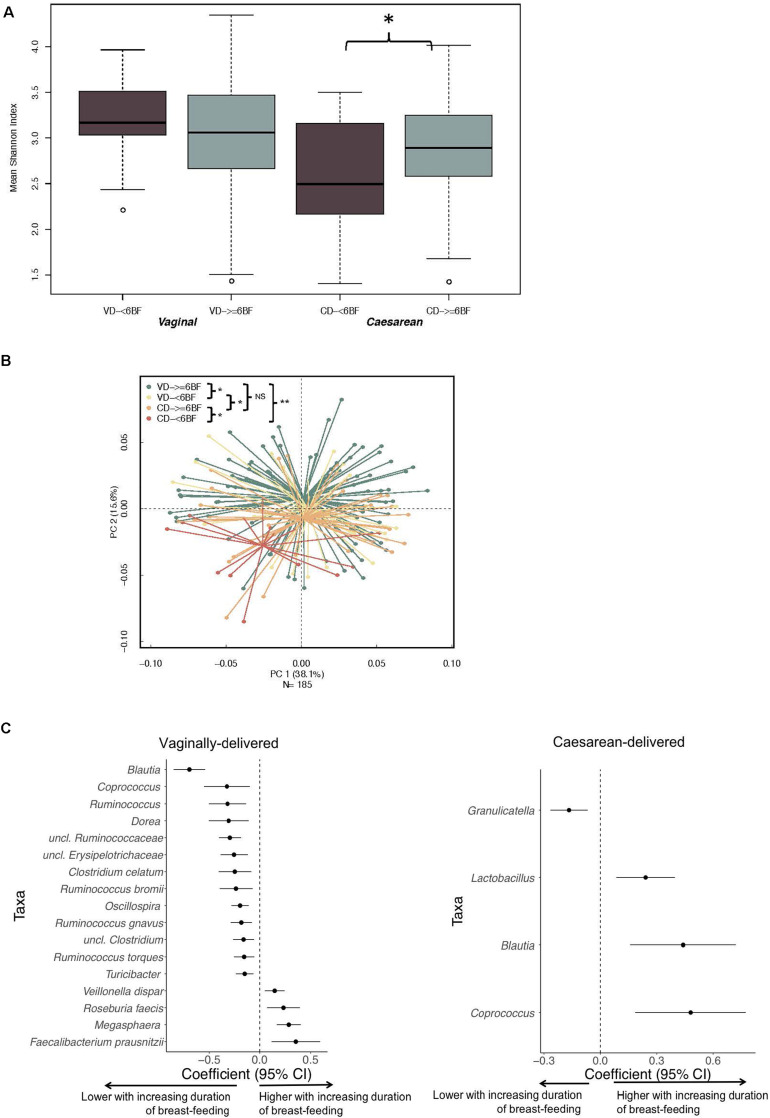
FIGURE 2.
The impact of breastfeeding duration on the developing microbiota over 1 year (characterized by 16S rRNA gene) differs by delivery mode. (A) Breastfeeding duration was significantly associated with 1-year alpha diversity indices for CD infants and not for VD infants. (B) Beta diversity of gut community profiles differed by feeding mode at 6 weeks and breast-feeding duration at 1 year as visualized with PCoA plots. Adjusted p-values are the result of the adonis2 model, adjusting for gestational age, early feeding mode and solid food introduction at the time of sample collection. (C) Differentially abundant taxa highlighting ASVs (at the genus level) significantly impacted by duration of breastfeeding for VD and CD infants adjusted for gestational age, early feeding mode and solid food introduction at the time of sample collection. Data was derived from utilizing all time-varying samples within a mixed effect model in MaAsLin. VD, vaginally delivered; CD, cesarean-delivered; VD- ≥6BF, vaginally delivered who breast-fed for >6 months; VD- <6BF, vaginally delivered who never breast-fed or breast-fed for <6 months; CD- ≥6BF, caesarean-delivered who breast-fed for ≥6 months; CD- ≥6BF, operatively delivered who never breast-fed or breast-fed for <6 months. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, NS not significant.