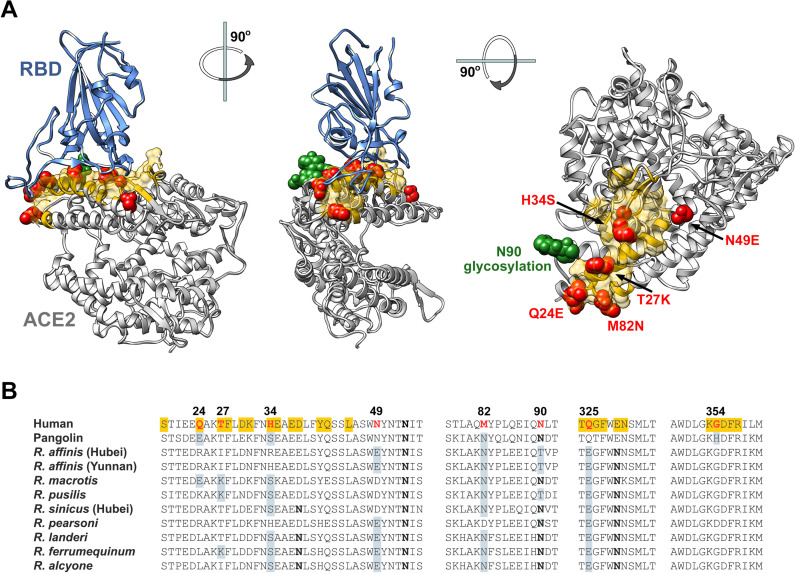
Fig 3. Sequence comparison of essential ACE2 residues for SARS2-RBD binding in horseshoe bats and pangolin ACE2 orthologs.
(A) Human ACE2 (grey) is shown bound to the SARS-CoV-2 RBD (blue), based on PDB accession number 6M0J (Lan et al., 2020). Yellow indicates the ACE2 surface that is within 5.5 Å of the RBD. Red indicates residues that vary between human and horseshoe bat species. Specific mutations are indicated in the rightmost figure. A glycosylation at asparagine 90, also characterized, is indicated in green. Figure shows successive 90-degree rotations around the vertical and horizontal axes, respectively. The RBD is removed from the rightmost figure for clarity. (B) Sequence of human ACE2 is aligned with the sequence of the pangolin ACE2 as well as selected horseshoe-bat ACE2 orthologs. Residues, directly associating or proximal to, the SARS-CoV-2 RBD are shown. Yellow highlights a residue that directly contacts the RBD. Red indicates human residues that were altered to the indicated pangolin or bat residues shown in gray and characterized in the subsequent figures. Bold indicates a glycosylated asparagine.