Fig. 1. LDKO mice exhibit a unique induction of N-glycosylation gene machinery.
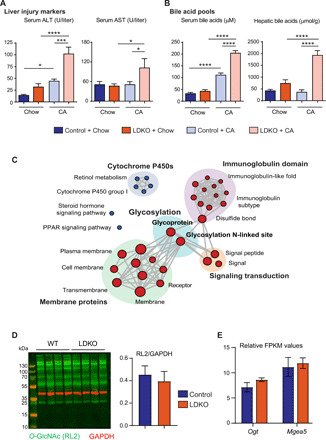
Biochemical characterization revealed (A) severe liver injury (marked by serum ALT and AST levels) and (B) bile acid accumulation in LDKO + CA mice compared to the controls (n = 6 to 11 mice per group, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001). (C) RNA-seq was performed on the livers of chow-fed control and LDKO mice. Functional clusters display enrichment of glycosylation upon Fxr-Shp deletion. Blue circles: down-regulated; red circles: up-regulated in LDKO mice (n = 3 mice per group). (D) Neither intracellular O-GlcNAcylation levels nor (E) the genes regulated O-GlcNAcylation, Ogt and Mgea5 were enhanced in LDKO mice (n = 3 to 4 mice per group; Student t test, P < 0.05 was considered significant). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. FPKM, fragments per kilobase million; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor.
