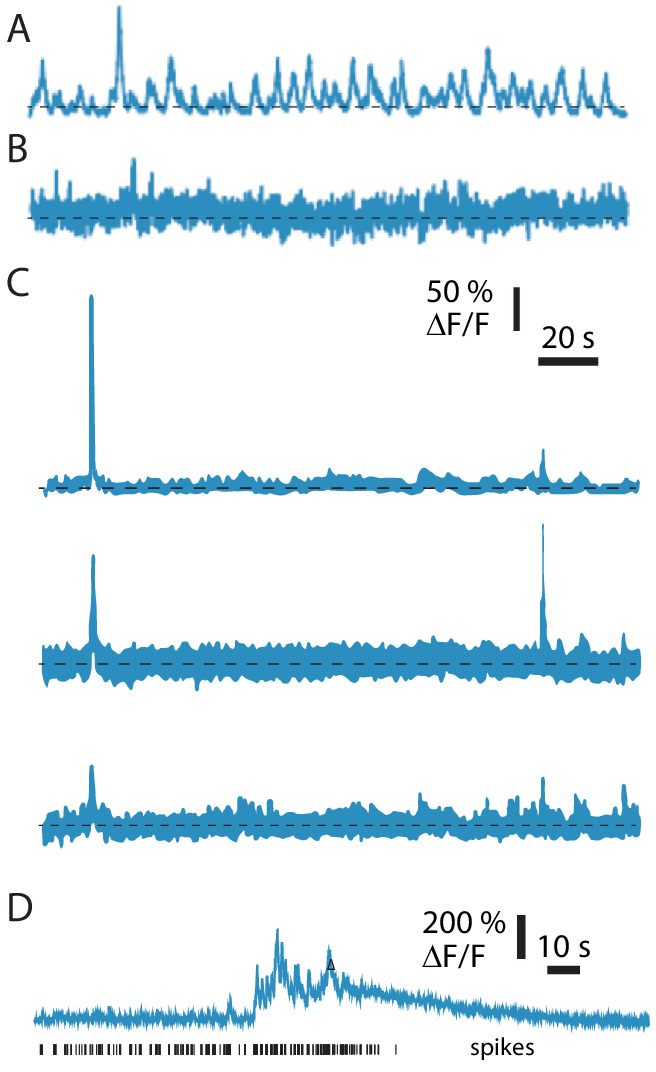
Figure 5. Downsampling mimics large field-of-view images.
(A) Original, high spatial and temporal resolution GCaMP6f image of an exemplar Cux2-f neuron. (B) 1 AP, 2 AP, and 3 AP traces for the same neuron. Thin lines, individual trials; thick line, mean. Dashed line, ΔF/F = 0. (C) Downsampled image of the same neuron. (D) Traces from the downsampled neuron. (E) Normalized distribution of baseline noise (robust standard deviation [rSTD]) for 48 downsampled neurons (red) and 11,816 layer 2/3 neurons from Emx1-f and Cux2-f mice in the Allen Brain Observatory (blue).
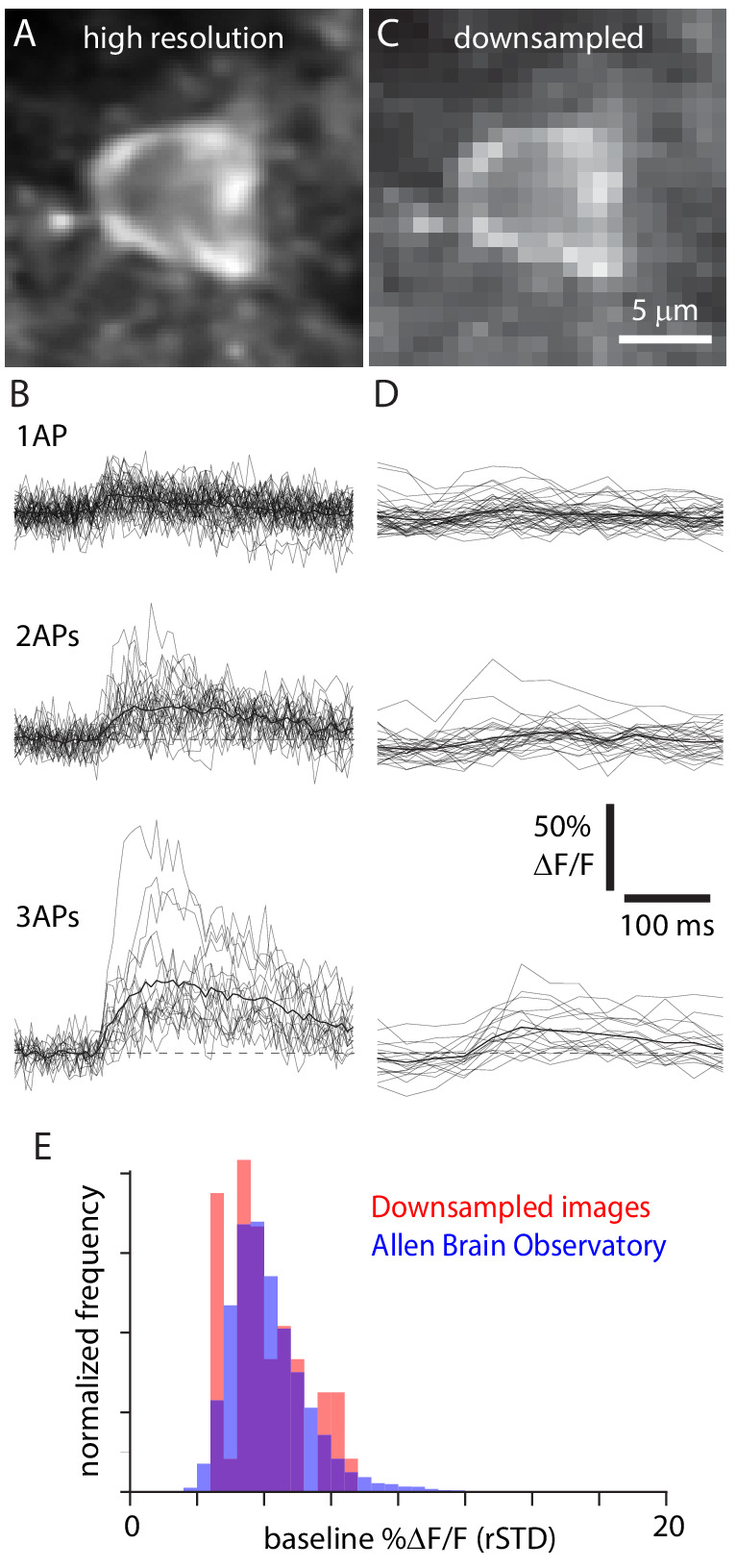
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Example fluorescence traces from image quality control procedures, implemented during image downsampling.