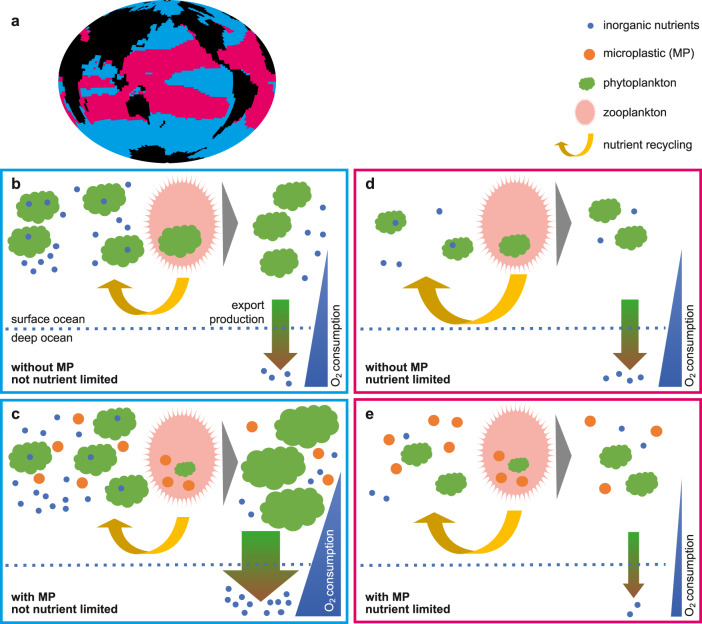
Fig. 3. Schematic of impact of zooplankton ingestion of microplastic on water column dissolved oxygen.
a Map view of macronutrient limited (pink) and nutrient-replete regions (blue). b In macronutrient-replete regions, e.g. the Southern Ocean, grazing pressure from zooplankton is a significant control on primary and export production. c Consumption of microplastic by zooplankton in macronutrient-replete environments reduces the grazing pressure on primary producers enhancing export production, that upon remineralization at depth consumes oxygen. d In macronutrient-limited environments primary producers rely on recycled nutrients supplied via the microbial loop and zooplankton excretion. e In the presence of zooplankton ingestion of microplastic a greater proportion of nutrients cycles through the temperature-sensitive microbial loop, leading to a decrease in export production which in turn drives a reduction in oxygen consumption at depth for remineralization.