Figure 2.
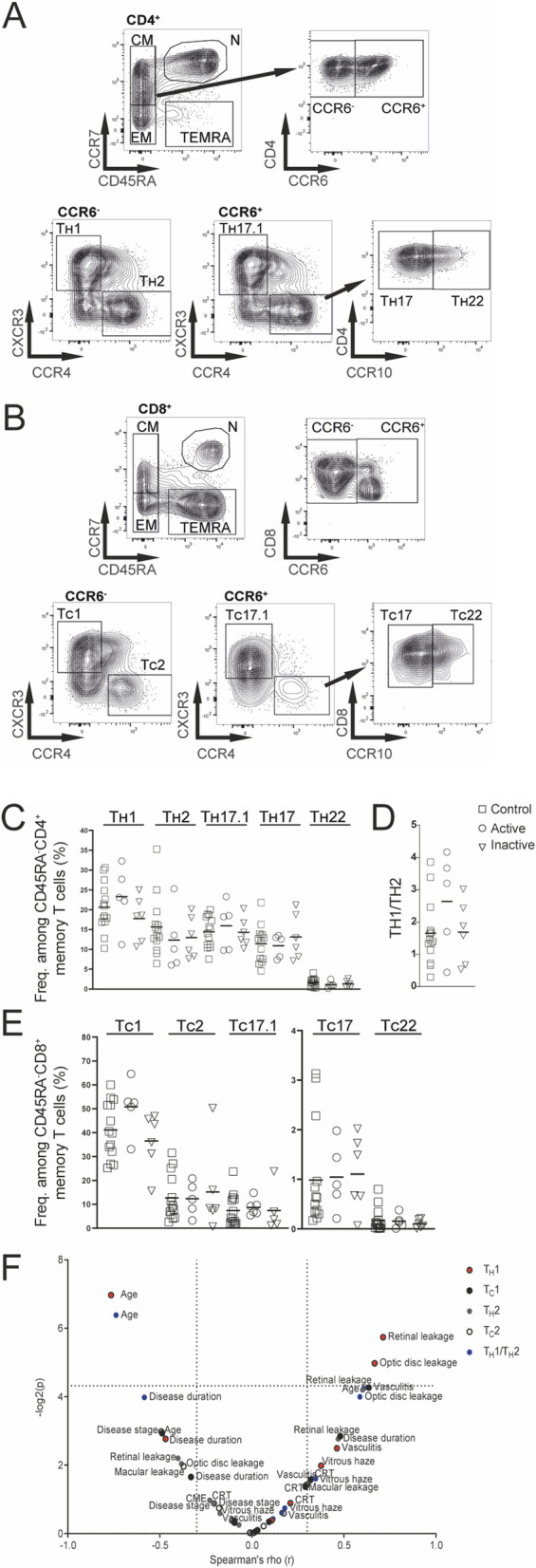
Inflammatory T-cell subsets in BSRC blood. (A) CD4+ and (B) CD8+ CD45RA− central and effector memory T cells were used to gate CCR6+ and CCR6− fractions. CCR6− cells were further distinguished in T1, based on CXCR3 expression or T2, based on CCR4 expression. CCR6+ cells were distinguished in T17.1, based on CXCR3 expression and T17 and T22 subsets were gated based on CCR4 and CCR10 expression. (C) Lines show median frequencies of CD4+ TH1, TH2, TH17.1, TH17 and TH22 T-cell subsets of controls and active/inactive BSRC patients. (D) The frequencies of TH1 and TH2 fractions were used to calculate a TH1/TH2 ratio. (E) Lines show median frequencies of CD8+ TC1, TC2, TC17.1, TC17 and TC22 T-cell subsets. (F) Volcanoplot (− log10) shows Spearman’s Rho correlation coefficient of immunological versus clinical parameters of TH1, TH2, TC1, TC2 T-cell populations and TH1/TH2 ratio of BSRC patients. BSRC birdshot retinochoroiditis, CM central memory, CME cystoid macula edema, CRT central retinal thickness, EM effector memory, N naïve, TC cytotoxic T cell, TH T-helper, TEMRA terminally differentiated effector memory CD45RA+.
