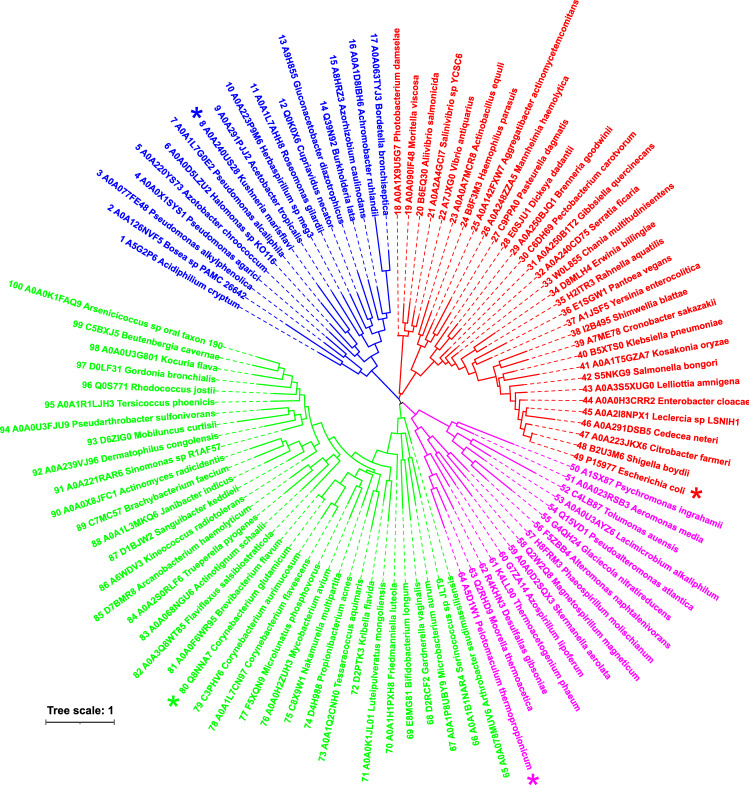
Fig. 3.
Evolutionary tree of the N-terminal domains of GH77 amylomaltases. The tree displays the relatedness of 100 unique non-redundant GH77 sequences (Table S1) containing the N-terminal domain corresponding to an immunoglobulin-like fold observed in crystal structures of E. coli (Pugsley and Dubreuil 1988; Weiss et al. 2015) and C. glutamicum amylomaltases (Srisimarat et al. 2011; Joo et al. 2016). Each protein is labelled by the UniProt accession number and the name of the organism. Four proteins, representing four clusters illustrated on the tree and each distinguished by different colours, are marked by an asterisk, i.e. amylomaltases from Kushneria marisflavi (blue), Escherichia coli (red), Pelotomaculum thermopropionicum (magenta) and Corynebacterium glutamicum (green). The tree is based on the alignment of the N-terminal domains (Fig. 2)