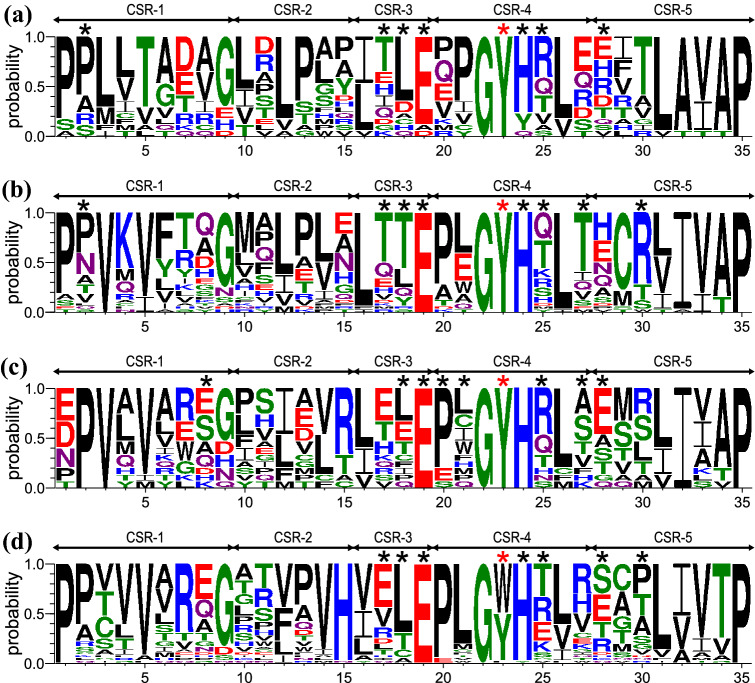
Fig. 4.
Sequence logos of N-terminal domains from individual clusters of family GH77 bacterial amylomaltases. The four groups (for details, see Table S1) are represented by a Kushneria marisflavi (Proteobacteria; ~ 70 residues long; 17 sequences); b Escherichia coli (Gammaproteobacteria; ~ 80 residues long; 32 sequences); c Pelotomaculum thermopropionicum (Firmicutes and Alphaproteobacteria ~ 100 residues long; 15 sequences); and d Corynebacterium glutamicum (Actinobacteria; ~ 90 residues long; 36 sequences). CSR-1, residues 1–9; CSR-2, residues 10–15; CSR-3, residues 16–19; CSR-4, residues 20–27; CSR-5, residues 28–35. The aromatic residue, marked by the red asterisk, corresponding to Tyr108 and Trp143 in E. coli and C. glutamicum amylomaltases, respectively, is potentially involved in stacking interactions with α-glucans. All other residues involved in hydrogen bonding contacts with docked α-glucans (G2, G3, G4 and β-CD; for details, see Table 1) are indicated by black asterisks