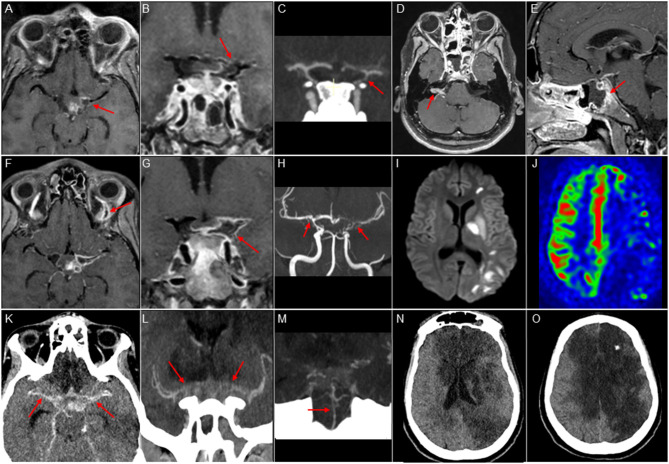
Figure 1.
Imaging features. Upper panel: MRI and CT scan at admission. (A,B,D,E): Cube T1 FatSat post Gadolinium contrast, axial (A,D), coronal (B), and sagittal (E) views. (C): Contrast-enhanced CT with arterial phase, coronal view. Vasculitis of the Circle of Willis: stenosis of the left internal carotid artery, middle cerebral artery, and anterior cerebral artery (A-C), with vessel wall enhancement (A,B). Right acoustic-facial neuritis (D, arrow), sphenoid sinusitis with adjacent osteitis (E, arrow). Medium panel: MRI after sudden right hemiplegia and aphasia. (F,G) Cube T1 FatSat post Gadolinium contrast, axial view; (H) 3D Time-of-Flight angio-MR coronal view; (I) DWI sequence, axial view; (J) Arterial Spin Labeling perfusion sequence, axial view. Recent arterial ischemic stroke in the left middle cerebral territory (I) with extended hypoperfusion (J), worsening of severe and bilateral vasculitis (F-H), and left ophthalmic vein thrombosis (F, arrow). Lower panel: CT scan at day 14. (K): post-contrast axial view; (L,M) angio-CT coronal view; (N,O): axial view. Worsening of the intracranial vasculitis (K-M), with basilar artery involvement (M). Large bilateral infarcts in anterior and middle cerebral artery territories (N,O).