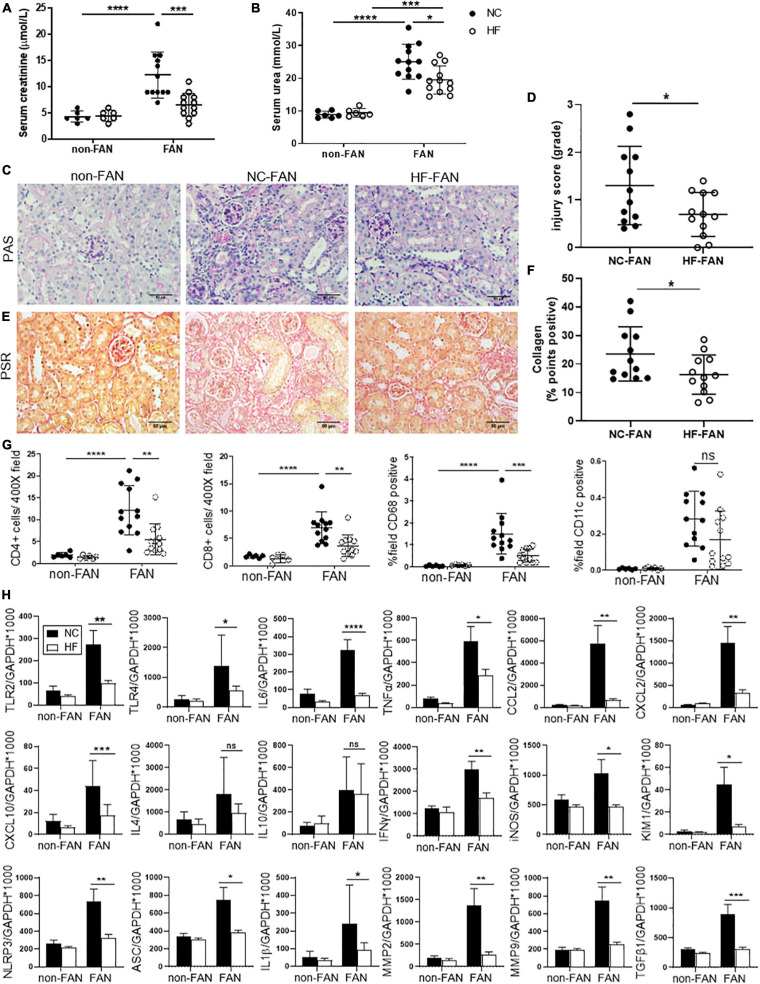
FIGURE 2.
HF fed mice exhibit less chronic inflammation at day 28 after FAN induced AKI. HF fed mice developed less chronic kidney injury at day 28 following FA-induced AKI, with lower serum creatinine (A), BUN (B) and histological injury scores assessed on PAS stained kidney sections (C,D) compared to NC fed FAN controls. Representative sections of kidney from FAN and non-FAN mice at day 28 demonstrating increased interstitial collagen deposition attenuated by HF feeding on PSR staining (E,F). Quantification of immunostaining for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, CD68+ macrophages and CD11c+ dendritic cells demonstrates significant infiltration in NC fed FAN kidneys. HF feeding significantly diminished T cell and CD68+ macrophage accumulation in FAN kidneys, with a trend toward diminished CD11c+ infiltrate (G). (H) mRNA expression of innate immune receptors (TLR2 and TLR4), pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL6, and IFNγ), chemokines (CCL2, CXCL2, and CXCL10), inflammatory mediator (iNOS), inflammasome components (NLRP3, ASC, and IL1β), renal proximal tubular injury marker (KIM1), and fibrosis related genes (TGFβ1, MMP2, and MMP9) were significantly reduced in HF fed FAN mice as compared to NC fed FAN controls. No significant difference was seen in Th2 cytokines (IL4 and IL10) following HF feeding. NC, vehicle (n = 6); HF, vehicle (n = 6); NC, FAN (n = 12); HF, FAN (n = 12). Photomicrographs at 400×, scale bar 50 μm. Data are shown as means ± SD or mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.