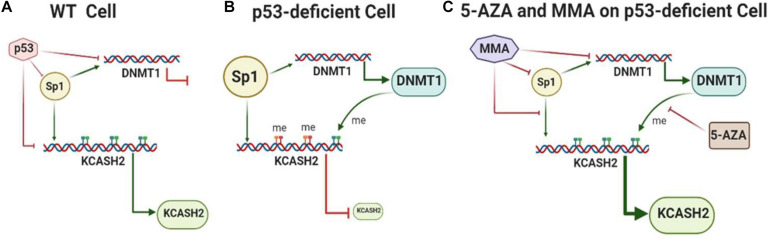
FIGURE 8.
Model of KCASH2 regulation in WT and p53-deficient cells. (A) In WT cells, transcriptional activity of the KCASH2 promoter is balanced by the effect of basal transcription sustained by Sp1 and suppression operated by p53. In this context, p53 also inhibits Sp1-dependent DNMT1 transcription, leaving the KCASH2 promoter accessible to transcription factors. (B) In p53-deficient cell, Sp1 is upregulated and leads to active DNMT1 transcription. The consequent methylation on CpG islands of the KCASH2 promoter inhibits Sp1 binding and its capability to activate KCASH2 transcription, resulting in low levels of KCASH2. (C) MMA and 5-AZA treatment in p53-deficient cells enhance KCASH2 transcription. MMA reduces Sp1 levels, and its binding and activation of the DNMT1 promoter. 5-AZA treatment leads to demethylation of the CpG island rendering KCASH2 promoter available for Sp1 binding and Sp1-mediated basal activation.