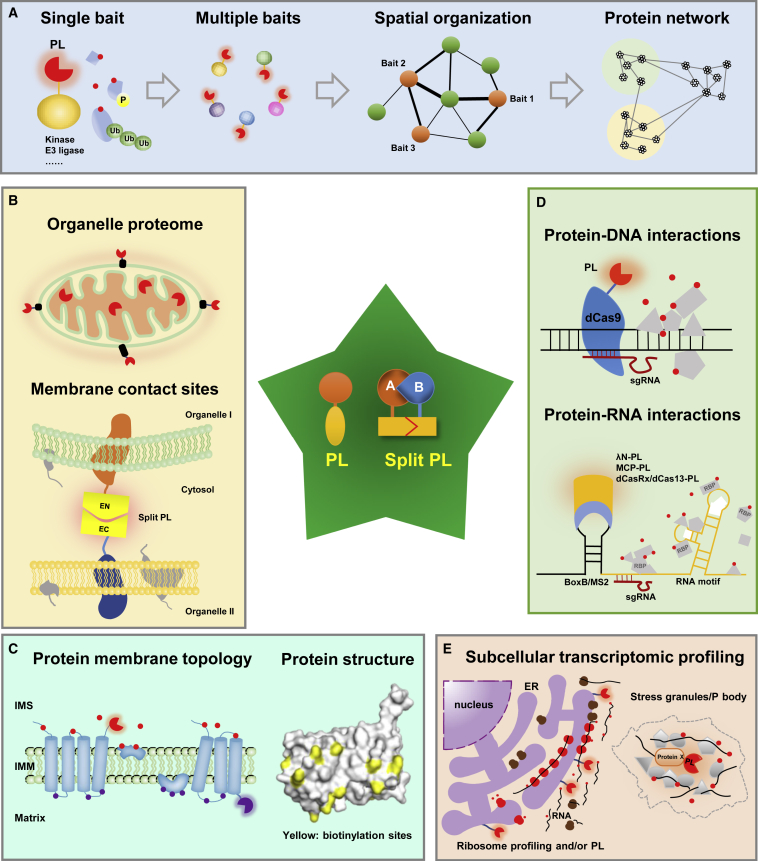
Figure 2.
Application of PL in probing diverse molecular interactions.
(A) Using PL for the identification of a single PPI, deciphering the spatial relationship of different proteins, and constructing protein interaction networks.
(B) Proteomic analysis of subcellular compartments and membrane contact sites by PL or split-PL.
(C) Application of PL to determine the topology of proteins and gain structural insights into the target protein. Due to the impermeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) to small molecules, PL will occur exclusively at either the IMS (red) or the matrix side (brown).
(D) Identification of proteins bound to a specific genomic locus or RNA motif by combining PL with other existing techniques.
(E) Application of PL to map the membrane-enclosed or membrane-less organelle RNAome together with other techniques, such as ribosome profiling. These RNAs can be either mRNAs for translation or noncoding RNAs.