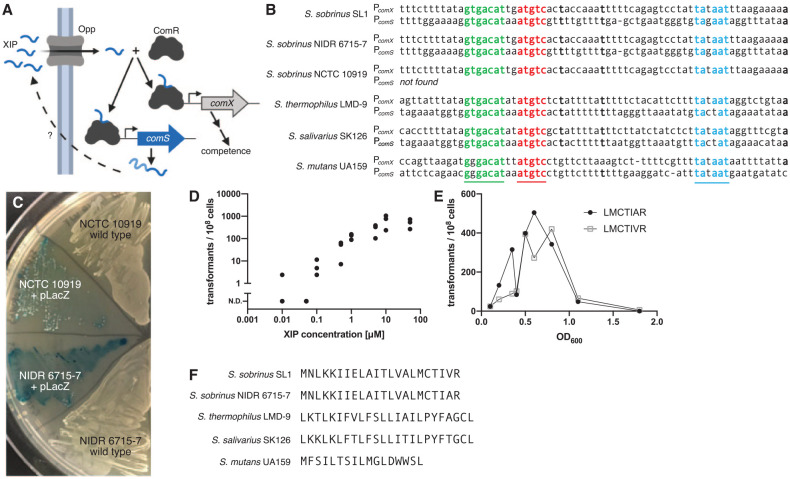
Figure 1.
The peptide XIP induces competence in Streptococcus sobrinus. (A) The ComRS competence pathway in Streptococcus mutans forms an autocrine signaling loop. An unknown protein cleaves the leader peptide from ComS and exports the XIP precursor. Activated XIP is imported, where it facilitates dimerization of the transcriptional regulator ComR. The ComR/XIP complex binds a DNA motif to promote transcription of comX and comS. (B) The ComR/XIP binding motif appears upstream of the sigma factor comX. Using this sequence, we identified a comS gene in 2 strains of S. sobrinus. The comS gene appears downstream of a homolog of the regulator comR. (C) S. sobrinus strains NIDR 6715-7 and NCTC 10919 can be transformed with exogenous XIP. Both strains were transformed with a plasmid expressing LacZ. When plated with X-gal, the plasmid-carrying strains produce a blue color, but the wild type strains do not. (D) The transformation efficiency of S. sobrinus strain NCTC 10919 increases with XIP concentration. Transformation assays used linear DNA with homology to regions flanking comR. No transformants were observed without XIP. (E) Transformation efficiency peaks in the midexponential phase. Transformation assays were performed with strain NCTC 10919 and the pLacZ plasmid (Appendix Fig. 1) by using the predicted XIP for strains SL1 (LMCTIVR) and NIDR 6715-7 (LMCTIAR). No XIP precursor gene (comS) is found in the NCTC 10919 genome. (F) The S. sobrinus ComS peptides differ from sequences in S. mutans, Streptococcus salivarius, and Streptococcus thermophilus. In particular, all previously known XIP sequences in streptococci contain 2 aromatic amino acids; the XIP in S. sobrinus has none.