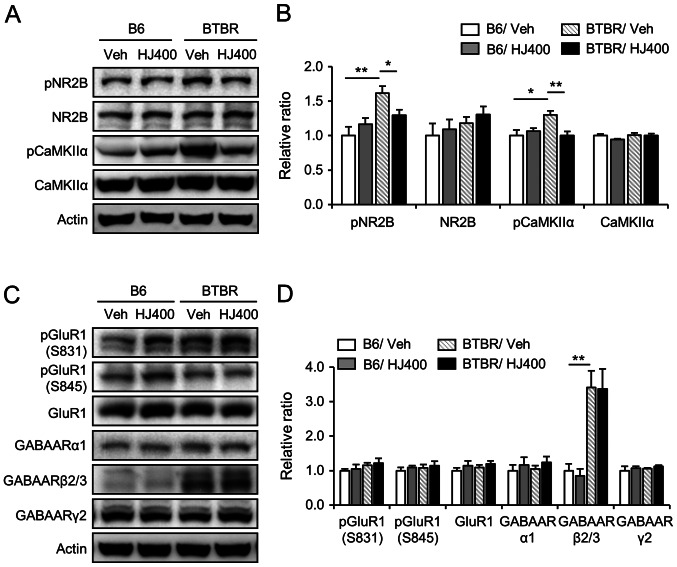
Figure 6.
Effects of HJ treatment on the phosphorylation of NR2B and CaMKIIα in the hippocampus of C57BL/6J and BTBR mice. Western blot analysis of NMDA receptor subunit NR2B, pNR2B (Tyr1472), CaMKIIα, pCaMKIIα, AMPA receptor subunit GluR1, pGluR1 (Ser831), pGluR1 (Ser845), and GABAA receptor subunits α1, β2/3, and γ2 in the hippocampus of the vehicle-treated (vehicle) and 400 mg/kg HJ-treated (HJ400) B6 or BTBR mice. Band densitometry values normalised to actin levels. (A) Representative image and (B) quantitative analysis of NMDA receptor subunit NR2B, pNR2B (Tyr1472), CaMKIIα, pCaMKIIα (Thr286) in the hippocampus of the vehicle-treated (vehicle) and 400 mg/kg HJ-treated (HJ400) B6 or BTBR mice. (C) Representative image and (D) quantitative analysis of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1, pGluR1 (Ser831), pGluR1 (Ser845), and GABAA receptor subunits α1, β2/3, and γ2 in the hippocampus of the vehicle-treated (vehicle) and 400 mg/kg HJ-treated (HJ400) B6 or BTBR mice. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. indicated group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. HJ, Humulus japonicus; NR2B, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; CaMKIIα, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit α; p, phosphorylated.