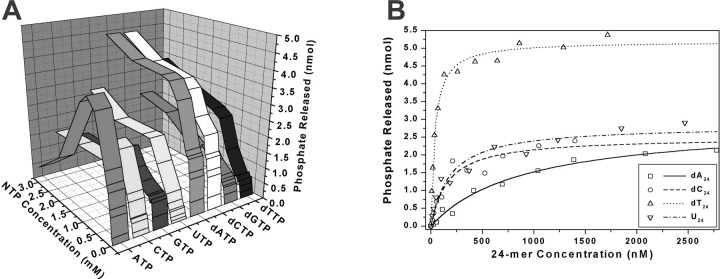
Fig. 3.
Effect of NTP and polynucleotide concentration on rate of NTP hydrolysis catalyzed by the SARS coronavirus NTPase/helicase.Panel A, hydrolysis of NTP by the SARS coronavirus NTPase/helicase versus NTP concentration versus NTP identity for eight different nucleotides. Data for the NTPase activity for each NTP over a range of NTP concentrations (0–3 mm) were fitted to a simple Michaelis-Menten model; the results are shown in Table I. Experimental conditions were: 25 μg/ml poly(U), 5 mm MgCl2, 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 6.6, 50-μl reaction volume, 0.4 pmol of helicase, 10-min reaction. Panel B, hydrolysis of dATP by the SARS coronavirus NTPase/helicase versus polynucleotide concentration for four different polynucleotides. Data are shown after subtraction of basal dATPase phosphate release. Data for the dATPase activity in the presence of each polynucleotide were fitted to a simple Michaelis-Menten model, with the fit shown by the four lines. Experimental conditions were: 1 mm dATP, 5 mm MgCl2, 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 6.6, 50-μl reaction volume, 0.7 pmol of SARS-CoV helicase, 10-min reaction.