Fig. 1.
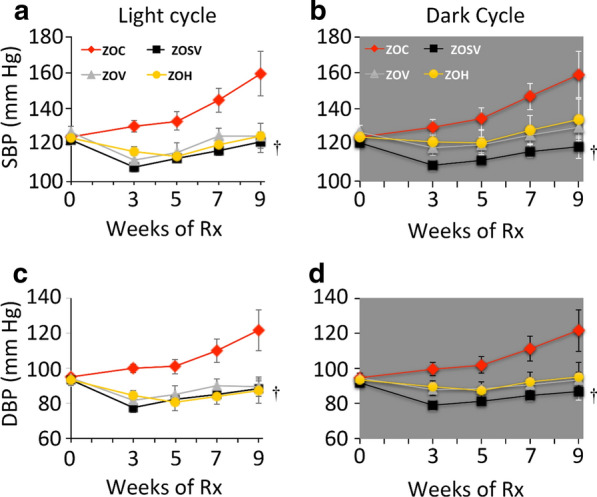
Ambulatory blood pressure was monitored periodically utilizing radio-telemetric transmitters. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure were recorded prior to the beginning of treatment and after 3, 5, 7 and 9 weeks of treatment during the light and dark cycles. SBP and DBP increased throughout the course of treatment in ZOC. After 9 weeks of treatment SBP and DBP were significantly reduced in ZOSV during the light and dark periods compared to ZOC (p < 0.05 indicated by the dagger (†) symbol). N = 4, 4, 3 and 4 for ZOC, ZOSV, ZOV and ZOH, respectively
