Figure 9.
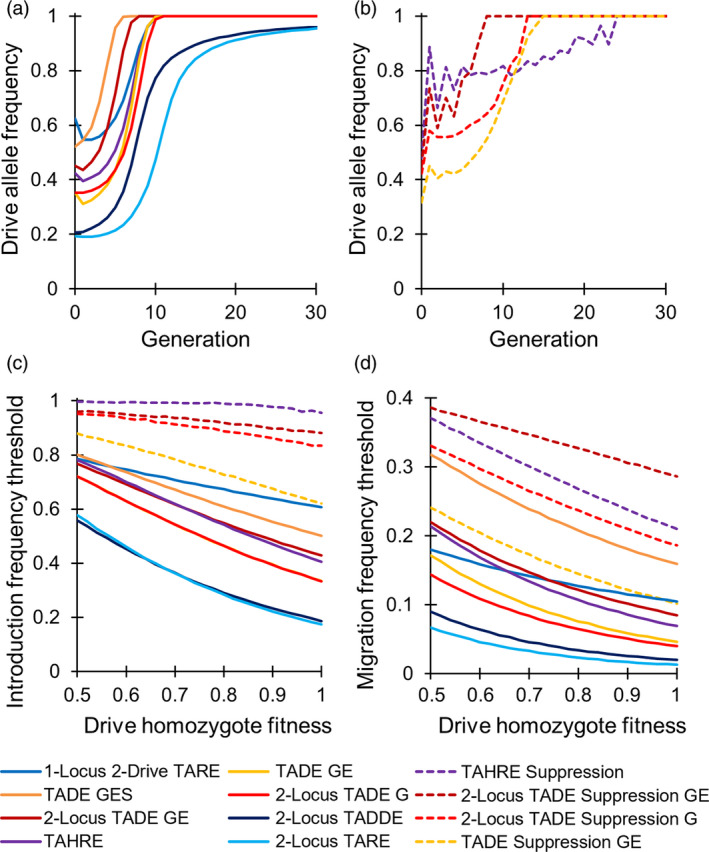
Dynamics of TA underdominance drives. (a) Example allele frequency trajectories for modification drives introduced at 2% above their introduction frequency thresholds in our population model. (b) Example allele frequency trajectories for suppression drives introduced at 2% above their invasion threshold frequency. (c) Invasion frequency thresholds (the frequency of introduced drive‐carrying individuals, as a fraction of the initial population, above which the drive will increase in frequency and below which the drive will be eliminated) and (d) Migration frequency thresholds (the per‐generation rate of migration of drive‐carrying individuals as a percentage of the initial population above which the drive will increase to a high frequency instead of remaining at a low equilibrium frequency). Note that the TADE GE and 2‐locus TADE G drives have the same thresholds. In modification systems, released individuals were homozygous for the drive. In suppression systems, individuals were heterozygous for the drive. G, germline‐only promoter; GE, promoter with germline and early embryo cutting (in the progeny of drive‐carrying females); GES, promoter that induces a high rate of somatic cleavage
