Fig. 4.
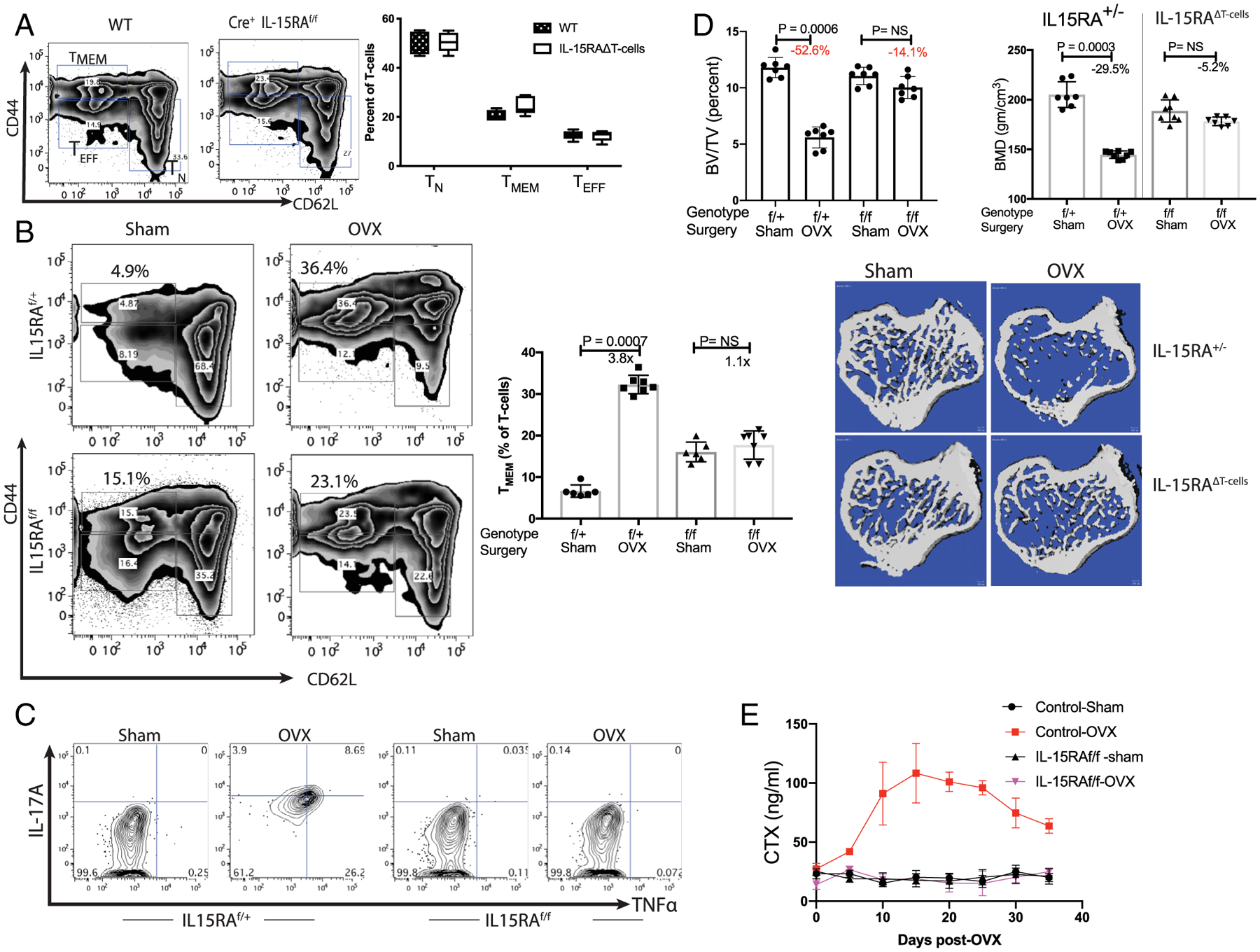
Ablation of IL-15 receptor α chain in T-cell prevents bone loss post-ovariectomy: IL15RAf/f mice were mated with Lck-Cre mice in two rounds of crosses to obtain Cre-positive IL15RAf/f, Cre+ IL15RAf/+ and Cre+ IL15RA+/+ littermates. The control (IL15RA sufficient) mice included both Cre+ homozygote (IL15RA+/+) and heterozygotes (IL15RAf/+) as they were phenotypically similar, if not identical, in assays used here (i.e. T-cell populations, IL-17A, TNFα induction and bone parameters). IL15RAf/f Cre+ mice are labeled as IL15RAΔT-cells in some panels. (A) No significant change in T-cell populations in IL15RAΔT-cells mice: Percent of T-cell subsets in the bone marrow of WT C57BL/6J and Cre+ IL15RAf/f in 10-week-old female mice were compared. No significant difference is observed in in bone marrow T-cells indicating that all T-cell subsets develop normally in the absence of IL15RA. Data representative of six mice/group is shown. (B) No change in TMEM subset is observed in IL15RA-deficient mice post-OVX: 12-week-old Cre-positive flox/flox (IL15RAf/f) or 1L15RA-sufficient mice were OVX or sham-operated. Mice were euthanized 3 weeks postsurgery and bone marrow T cells analyzed by flow-cytometry. Two-factor ANOVA (genotype and surgery) indicates that genotype (baseline values) account for 1.29% of the variance (p < .03) and surgery accounts for 55.6% of the variance (p < .0001); the interaction term accounts for 37.8% (p < .0001) indicating that OVX had a larger effect in WT but not in mutant mice. These results are consistent with the model in Fig. 3D, where an increase in T (CD45+ CD3+ CD44high CD62Llow) is observed in the control mice, the TMEM in IL15RAΔT-cells mice do not change. (C) T-cells with IL15RA deficiency do not express IL-17A and TNFα: While Cre+IL15RAf/+ mice express IL-17A and TNFα, these cytokines are not observed in OVX Cre+IL15RAf/f mice. (D) IL15RAΔT-cell mice maintain bone mass post-OVX: 12-week-old female Cre+IL15RAf/f and control liter-mates (Cre+IL15RAf/+) were sham-operated or OVX. Mice were sacrificed 3.5 weeks post-OVX and were evaluated by measuring bone-volume over total-volume (% BV/TV) and BMD. For BV/TV a two-factor ANOVA indicates that genotype contributed 13.15% (p < .0001) of the variance, surgery accounted for 50.3% (p < .0001) of the variance and the interaction term accounted for 25.9% (p < .0001). While control mice lost bone mass, mice with T-cell deficient in IL15RA maintained bone mass. Trabecular parameters by μCT of tibias is shown in Table 1. (E) Time course of CTX post-OVX in IL15RA sufficient and T-cell specific 1L15RA-deficient mice: Although control IL15RA-sufficient mice lost bone, no bone loss is observed in IL15RA-deficient mice, demonstrating the role of inflammation in promoting bone loss.
