Fig. 2.
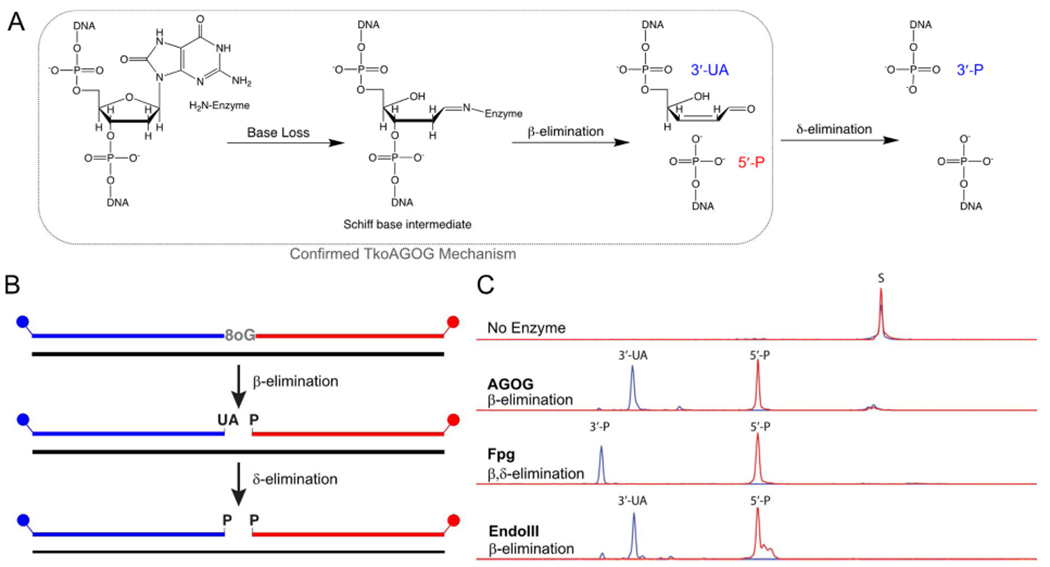
TkoAGOG is a bifunctional 8oxoG DNA glycosylase. A, Proposed enzymatic mechanism of a bifunctional 8oxoG DNA glycosylase, where 8oxoG nucleobase loss is followed by a Schiff base intermediate that undergoes β-elimination and for some DNA glycosylases such as Fpg further δ-elimination. The confirmed TkoAGOG mechanism is boxed in grey B, A 60-nt, 5’-FAM (blue), 3’-ROX (red) labeled dsDNA substrate with a centralized 8oxoG:C (or dU:G) was incubated for 30 min with either TkoAGOG at 65 °C, Fpg at 37 °C, or UDG/EndoIII at 37 °C and quenched with Formamide + EDTA, allowing for visualization of the base excision glycosylase and AP lyase activities. C, The conversion of 60-nt substrate to the 5’-FAM and 3’-ROX products after incubation with TkoAGOG, Fpg, or UDG/EndoIII.
