Figure 6.
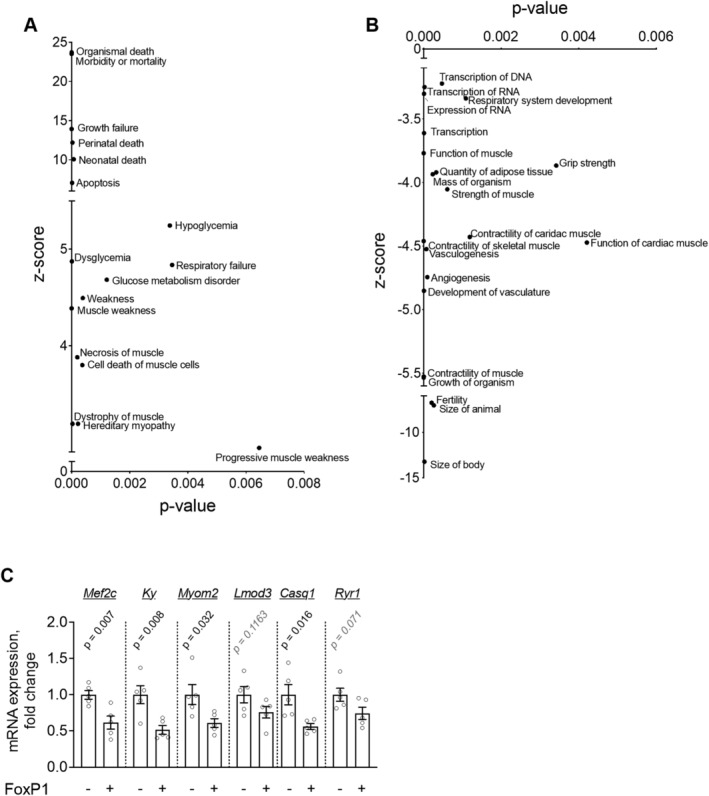
Acute FoxP1 over‐expression in skeletal muscle leads to dysregulation of skeletal muscle homeostatic pathways. Mouse tibialis anterior muscles were transfected with a FoxP1 plasmid or empty vector and microarray analyses were conducted on pooled samples (n = 3 per group). (A‐B) IPA enriched diseases and functions that are up‐regulated (A) and down‐regulated (B) in response to acute FoxP1 over‐expression. (C) RT‐qPCR validation for selected genes involved in muscle structural development, function, and maintenance. Depending on data distribution, unpaired two‐tailed t‐tests or Mann–Whitney tests were performed to test for statistical differences between groups. Data are reported as mean ± SEM.
