Figure 3.
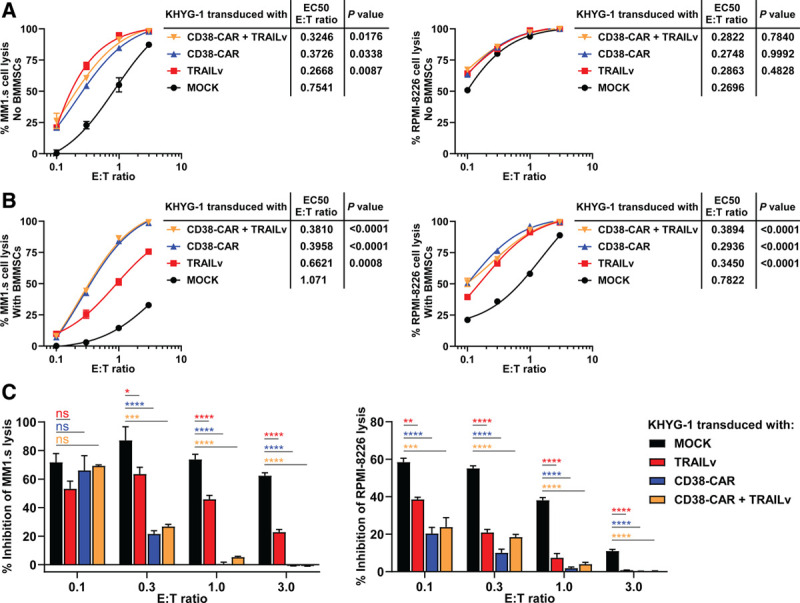
BMMSC-mediated resistance against KHYG-1 NK cells is significantly reduced by the incorporation of CD38-specific CAR or DR5-specific TRAILv. LUC-transduced MM1.s and RPMI-8226 cells were cultured in the absence (A) or presence (B) of BMMSCs and treated with serial E:T ratios of KHYG-1 cells that expressed MOCK control, CD38-CAR and TRAILv. MM cell survival was determined by BLI, 24 hours after treatment. The half maximal effective E:T ratios (EC50) of modulated KHYG-1 NK cells were compared with EC50 values of MOCK control using one-way ANOVA. (C) Results represent the percentages of inhibition of MM cell lysis (or MM cell survival) in the presence of BMMSCs. Percentages of inhibition were compared with MOCK control using one-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.0005; ****P < 0.0001). Results are representative of 2 independent assays. Error bars represent means with SEM of triplicate cultures. BLI = bioluminescence imaging; BMMNC = bone marrow mononuclear cells; BMMSC = bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell; CAR = chimeric antigen receptor; CI = Combination Index; LUC = Luciferase; MM = multiple myeloma; ns = not significant; PBMC = peripheral blood mononuclear cell.
