Fig 2. Crossing design for mapping unlinked modifiers of heterospecific (Dd) and conspecific (DD-) drive.
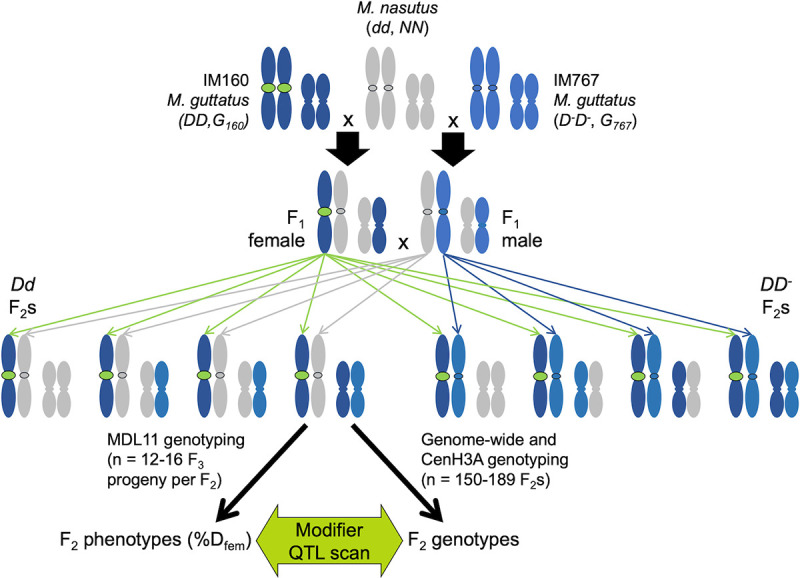
Two pairs of chromosomes are shown: Chromosome 11 with the centromeric MDL11 locus outlined in black and a second pair representing the rest of the genome. D (IM160; dark blue and green) and D- (IM767; pale blue) lines of M. guttatus were crossed to M. nasutus (grey) to generate heterospecific F1 hybrids. Intercrossing the F1s produced an F2 mapping population segregating only DD- and Dd at MDL11 due to strong heterospecific drive through the female Dd parent: green arrows) and in Mendelian ratios elsewhere (blue and grey arrows). F2s were genotyped genome-wide (scored as NN, NG, GG) and at a marker that could distinguish the alternative CenH3A alleles donated by the IM160 and IM767 parents (G160 and G767, respectively).
