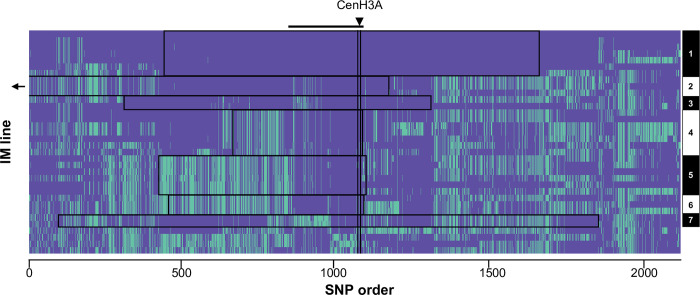
Fig 4. CenH3A exhibits a recent selective sweep, consistent with evolution in response to costly D spread.
Exonic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across a 496 kilobase (kb) region flanking CenH3A (13.5–14 Mb on Chromosome 14) are displayed for each of 34 lines from the Iron Mountain population of M. guttatus. The ~2000 SNPs are ordered by genomic position, but the x-axis is not scaled to physical or genetic distance. SNPs are coded according to whether they match (purple) or differ from (green) the haplotype of IM1054, which bears one of the most common CenH3A-flanking haplotypes. The arrowhead and horizontal line mark the location of CenH3A. The seven haplotypes (1–7) were assigned manually and are outlined in black boxes. For visual resolution around CenH3A, the longest haplotype (> 620kb) was truncated. Haplotype details are given in S6 Table.