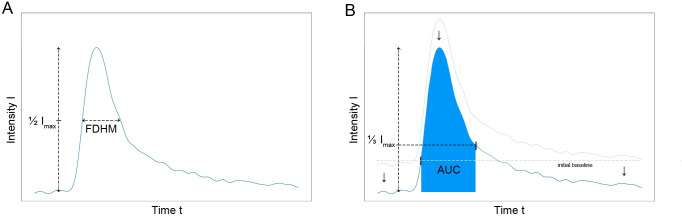
Fig 3. Algorithms for velocity calculation.
(A) FDHM method: The FDHM is the time span at which at least half of the maximum intensity is present. The mean velocity can then be calculated by including the size of the FOV in longitudinal direction. (B) Tracer dilution method: The flow rate can be calculated by dividing a calibration constant by the area under the curve (AUC) of the signal intensity over time curve. The first border of the AUC is the intersection of the mean intensity of the initial baseline and the baseline subtracted intensity over time curve. The end of the AUC is defined as the frame at which 33% of the maximum signal intensity is present during signal decline after the peak. The computed flow rate can then by converted to the mean velocity by including the inner diameter of the phantoms.