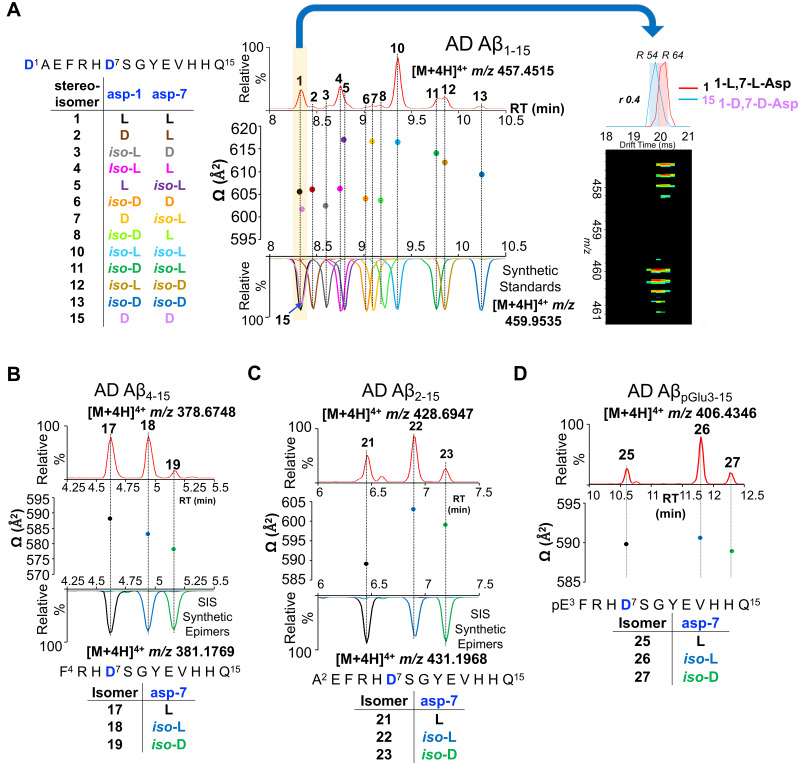
Figure 2.
Ion-mobility of amyloid-β isomers. Two-dimensional representation of RT−ion mobility high-resolution mass spectrometry (2D-LC-IMS-MS) results of extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of N-terminal Aβ peptides present in Alzheimer’s disease brain. (A) 2D-LC-IMS-MS of Aβ1–15 [M + 4H]4+m/z 457.4515 from formic acid fraction of human Alzheimer’s disease case illustrating the diversity of the isomerized Asp-1 and Asp-7 residues. The most abundant endogenous isomer of Aβ1–15 (top red panel) were characterized by comparing their chromatographic separation (co-elution) and their DTCCSN2 (Å2) with the synthetic standards (bottom multiple colour panel). The alignment of both the LC as well as the DTCCSN2 (Å2) reveal the most abundant endogenous isomers of Aβ1–15 in the FA fraction are 1,7-l-Asp (1), 1-iso-l, 7-l-Asp (4), 1-l, 7-iso-l-Asp (5), 1-iso-l, 7-iso-l-Asp (10), 1-iso-d, 7-iso-l-Asp (11), 1-iso-l, 7-iso-d-Asp (12) and 1-iso-d, 7-iso-d-Asp (13). The epimerized peptides 1-d, 7-l-Asp (2), 1-iso-l, 7-d-Asp (3), 1-iso-d, 7-d-Asp (6), 1-d, 7-iso-d-Asp (7) and 1-iso-d, 7-l-Asp (8) are minor constituents. The highlighted (yellow) LC-MS region depicts co-elution of native 1-l, 7-l-Asp (1) and 1-d, 7-d-Asp (15) at 8.3 min, although minute ΔDTCCSN2 ∼ 5 indicates that endogenous species corresponds to 1-l, 7-l-Asp (1) native Aβ1–15. (B) 2D-LC-IMS-MS representation of endogenous Aβ4–15 [M + 4H]4+m/z 378.6748 (top red panel) compared to isomerized synthetic standards (bottom panel), (C) Aβ2–15 [M + 4H]4+m/z 428.6947 (top red panel) compared to isomerized synthetic peptide standards (bottom panel) and (D) endogenous AβpGlu3–15 [M + 4H]4+m/z 406.4328 (top LC panel, red). DTCCSN2 (Ω in Å2) are shown for the corresponding isomerized peptides for clarity.