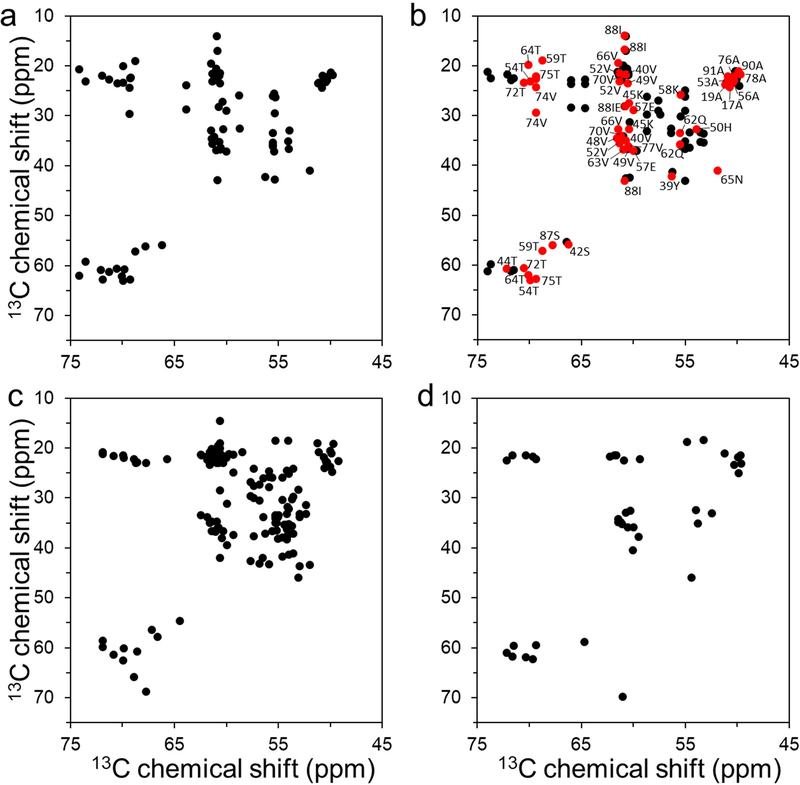
Figure 1.
Overview of aliphatic region of 2D 13C - 13C DARR NMR spectra of uniformly 13C/15N labeled α-synuclein filament polymorphs. (a) Tau-promoted α-synuclein polymorph. (b) Fibril-type α-synuclein polymorph (BMRB 18860).[25] Cross-peaks with similar NMR resonances for the tau-promoted α-synuclein polymorph and ribbon-type polymorph are colored in red with assignment (BMRB 18860). (c) Ribbon-type α-synuclein polymorph (BMRB 17498).[38] (d) Greek-key type α-synuclein polymorph (BMRB 25518).[9] The ribbon- and fibril-type polymorphs of α-synuclein have distinct molecular packing arrangement and intermolecular interactions.[25, 39] The NMR cross-peaks were drawn using our experimental DARR spectrum for the tau-promoted filaments (a) and chemical shifts reported in BMRB for the previously reported DARR spectra of α-synuclein filaments (b – d).