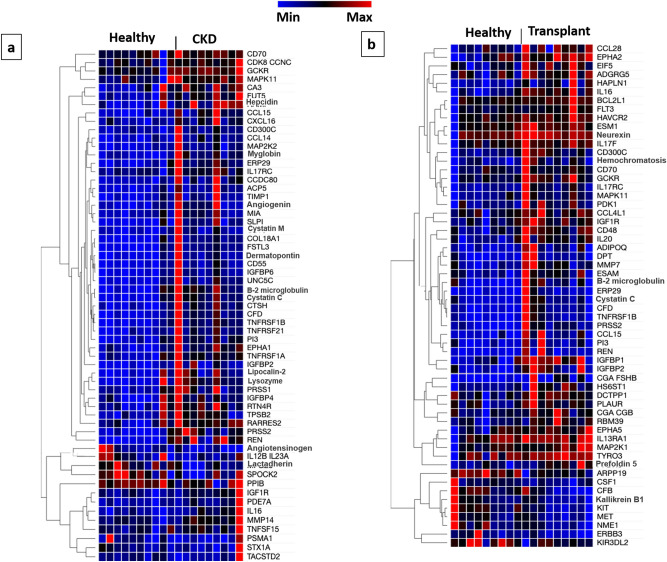
Figure 4.
Extracellular vesicle proteins differing between healthy controls and CKD. (a) shows the proteins found to be significantly different in the EVs of the patients with stage 3 or 4 CKD as compared to the healthy controls. (b) illustrates the proteins found to be significantly different in the EVs of the subjects with post-transplant CKD versus the healthy controls. The heat map was created via Morpheus, https://software.broadinstitute.org/morpheus. ABV: CKD: chronic kidney disease, Transplant: post-transplant CKD, CDK8/CCNC: cyclin C, GCKR: glucokinase regulator, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, CA: carbonic anhydrase, FUT: fucosyltransferase, CCL15: Chemokine Ligand 15, CXCL16: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16, CCL14: C–C Motif Chemokine Ligand 14, MAP2K: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, ERP29: endoplasmic reticulum protein 29, IL-17 RC: interleukin 17 receptor C, CCDC80: coiled-coil domain containing 80, ACP5: acid phosphatase 5, TIMP-1: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases, MIA: melanoma inhibitory activity, SLP1: secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, COL18: collagen 18, FSTL: Follistatin-related protein, CD55/DAF: complement decay-accelerating factor, IGFBP: insulin-like growth factor binding protein, UNC5C: Unc-5 Netrin Receptor C, CTSH: cathepsin H, CFD: complement factor D, TNFRSF1B: tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B, TNFRSF21: tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21, PI: peptidase inhibitor, EPHA: ephrin type-A receptor, TNFRSF1A: tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A, PRSS: serine protease, RTN4R: Reticulon 4 Receptor, TSPB2: tryptase beta-2, RARRES-2: retinoic acid receptor responder protein 2, REN: renin precursor, IL12B IL23A: reactome with interleukin-12B and interleukin-23A, SPOCK2: osteonectin, PPIB: Peptidylprolyl Isomerase B, IGF-1R: insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, PDE7A: Phosphodiesterase 7A, MMP: matrix metalloproteinase, TNFRSF15: tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 15, PSMA: Proteasome Subunit Alpha, STX1A: Shiga toxin type 1 A, TACSTD: Tumor Associated Calcium Signal Transducer, CCL28: C–C motif chemokine 28, EIF5: Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5, ADGRG5:Adhesion G Protein-Coupled Receptor G5, HAPLN1: hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1, BCL2L1: Bcl-2-like 1, FLT: fms-like tyrosine kinase, HAVCR: Hepatitis A Virus Cellular Receptor, ESM: endothelial cell specific molecule, PDK: phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase, CCL4L1: C–C Motif Chemokine Ligand 4 Like 1, ADIPOQ: Adiponectin, C1Q And Collagen Domain Containing, ESAM: endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule, CGA FSH-β: chorionic gonadotropin follicle-stimulating hormone-β, HS6ST: heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase, DCTPP1: dCTP pyrophosphatase-1, PLAUR: plasminogen activator, urokinase receptor, CGA CGB: chromogranin A and chromogranin B, RBM: RNA-binding protein, ARPP19: cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein-19, CSF: colony stimulating factor, CFB: complement factor B, KIT: tyrosine-protein kinase kit, MET: tyrosine-protein kinase Met, NME: Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase, ERBB3: erythroblastosis oncogene B-3, KIR3DL2: Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Three Ig Domains And Long Cytoplasmic Tail 2.