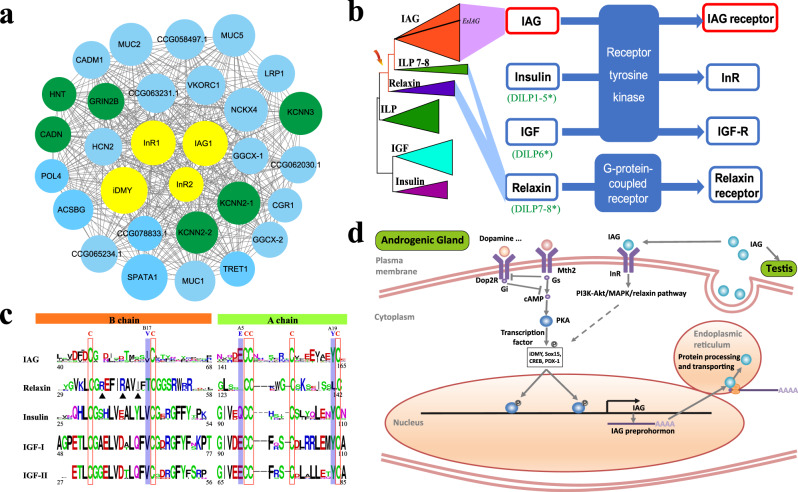
Fig. 5. The molecular regulation of AG.
a The co-expression network of the AG-related module (midnightblue, see Supplementary Data 13). The midnightblue module contains 216 genes, of which 30 genes with the highest intramodular connectivity are chosen for network display. IAG-related receptors and transcription factors are labeled in yellow. The neuron or axon-related genes are labeled in green. b Insulin-like peptides and their receptors. The insulin-like peptide (ILP) is subdivided into IAG, insulins, insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and relaxins on the basis of primary structure, processing and receptor binding preferences. c Conserved sites of crustacean IAG, and vertebrate relaxin, insulin and IGF-1 and IGF-II. The key functional sites for receptor binding are indicated by triangles. The amino acid numbers are with reference to IAG of Litopenaeus vannamei and other insulin members of human125. d The predicted synthesis and secretion pathway of IAG. Mth2 methuselah, PKA protein kinase A, Dop2R dopamine D2-like receptor, Gs guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha, Gi guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha, iDMY invertebrate sex-linked (Y-linked) Dmrt gene, Sox15 SRY-Box 15, CREB cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein, PDX-1 insulin promoter factor 1, InR insulin-like receptor.