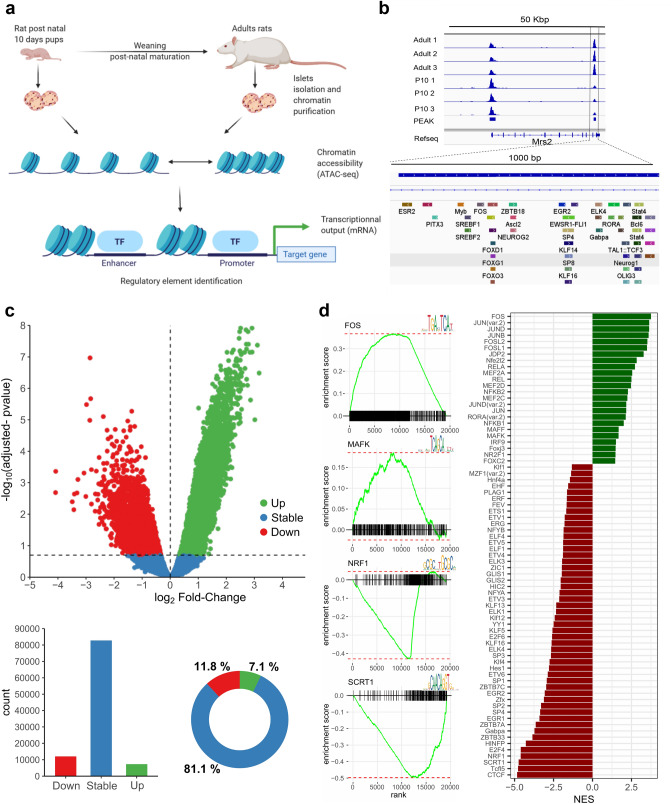
Figure 1.
ATAC-seq successfully identified accessible sites (ACS) and transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) motif associated with pancreatic islet maturation. (a) Summary of the experimental design. Nuclei were extracted from the islets of 3 adult rats and 3 litters of rat pups at postnatal day 10 (P10) to perform the Tn5 reaction as described in51 and prepare the library for sequencing. The computational pipeline involved a quality control of the sequencing data followed by read alignment to the rat reference genome (Rn5 assembly). ACS were identified using the peak calling tool MACS217 and quantified for each sample separately. The ACS sequences were scanned using FIMO20 and analyzed to identify TFBS motifs that are implicated in the islet maturation process and in related pathways (See methods). (b) Example of identified ACS. The ACS nearby Mrs2 transcription end site is significantly higher in adult rats. This ACS contains several TFBS motifs. (c) Differential analysis of Trn5 integrations in accessible sites. On the top, the volcano plot representation of the log2 fold-change of Trn5 integration between P10 and adult rat islets in the x-axis, and the FDR adjusted p-value in the y-axis. ACS more accessible in adults are represented in green (Up), those more accessible in P10 in red (Down), and those remaining stable in blue (p-value < 0.05, FDR < 0.2, n = 3). Below, the barplot of the number of ACS changing along postnatal maturation and the donut plot of the percentage of Up, Down and stable ACS. (d) Motif enrichment analysis in ACS identified putative regulators of postnatal pancreatic islet maturation. The left panels represent four enriched TFBS motifs. The right panel represents the FGSEA normalized enrichment score for top enriched motifs (FGSEA adjusted p-value < 0.05). See also Supplementary Figure S1 and Supplementary Table 1,2,3.