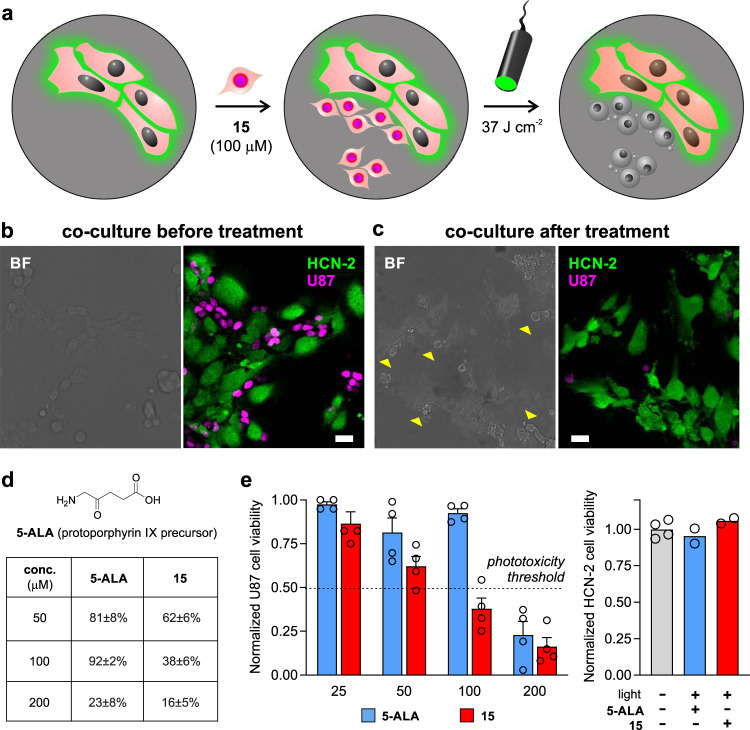
Fig. 5. Compound 15 selectively ablates human glioblastoma cancer cells under clinical PDT conditions and in the presence of non-cancerous human brain cells.
a Procedure for coculturing human non-cancerous brain HCN-2 cells (stained with CellMask Green) and human glioblastoma U87-nlsCrimson cells. Cocultures (15,000 HCN-2 cells and 10,000 U87 cells per well) were incubated with compound 15 (100 μM) and illuminated with ThorLabs M530L3 LED (37 J cm−2). The fluorescence emission from E2Crimson is reduced in U87-nlsCrimson glioblastoma cells upon cell death. (b, c) Representative brightfield and fluorescent confocal microscopy images (from three independent experiments) of cocultured HCN-2 (green, λem: 520 nm) and U87-nlsCrimson (magenta, λem: 645 nm) before (b) and after treatment (c). Yellow arrowheads in (c) highlight dead U87h cells devoid of Crimson fluorescence. Scale bars: 10 μm. d Phototoxicity analysis under different concentrations of compound 15 and 5-ALA in U87 glioblastoma cells (20,000 cells/well) using the same irradiation settings (10 mW, 37 J cm−2). Data presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). e HCN-2 cell viability (10,000 cells/well) after incubation with concentrations under the phototoxicity threshold [i.e., compound 15 (100 μM, red) and 5-ALA (200 μM, blue)] and light exposure (37 J cm−2). Data presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 4 independent experiments). Source data are available.