Figure 1.
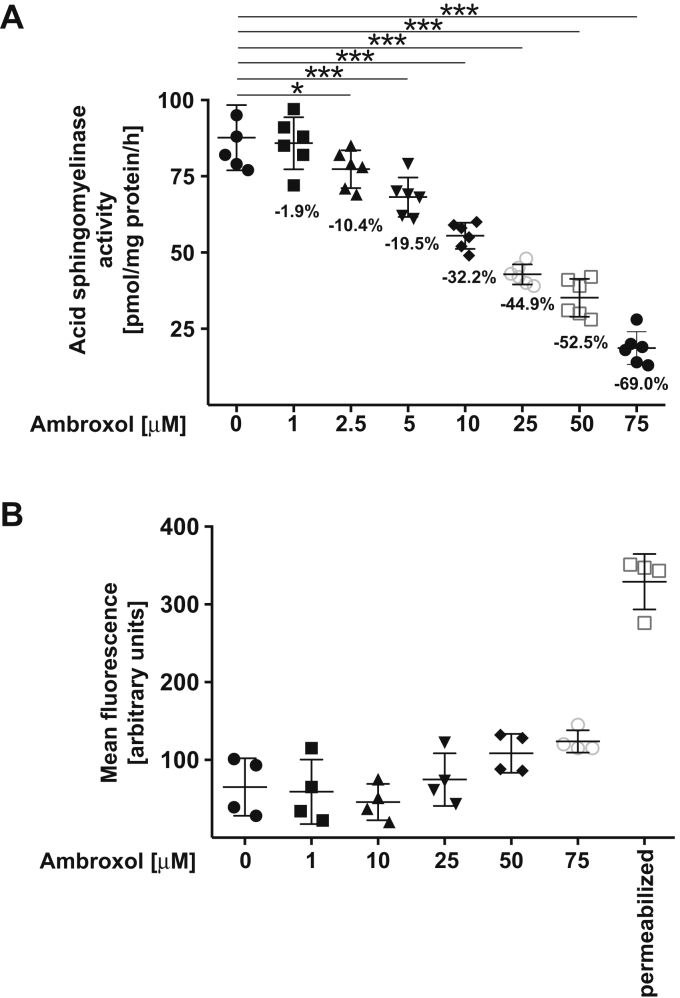
Ambroxol reduces the activity of the acid sphingomyelinase.A, Vero-E6 cells were incubated with 1, 2.5, 5, 10, 25, 50, or 75 μM ambroxol or with solvent (0) for 60 min. Cells were lysed in 250 mM sodium acetate (pH 5.0) and 0.2% NP-40, and acid sphingomyelinase activity was determined by measuring the consumption of added [14C]sphingomyelin. The percent decrease of acid sphingomyelinase activity is given for easier quantification. Shown are the means ± SD of the acid sphingomyelinase activities from six independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ANOVA followed by post hoc Student's t tests. B, ambroxol did not exhibit cytotoxicity after treatment for 24 h. Cells were exposed for 24 h to 1, 10, 25, 50, or 75 μM ambroxol, and toxicity was measured by FITC–annexin V staining. FITC–annexin V staining was analyzed by flow cytometry. Permeabilized cells served as positive controls for the FITC–annexin V staining. Shown are means ± SD of the fluorescence (in arbitrary units) in the flow cytometry studies (n = 4); ANOVA, followed by post hoc Student's t tests. Results are presented in arbitrary units (a.u.). NP-40, Nonidet P40.