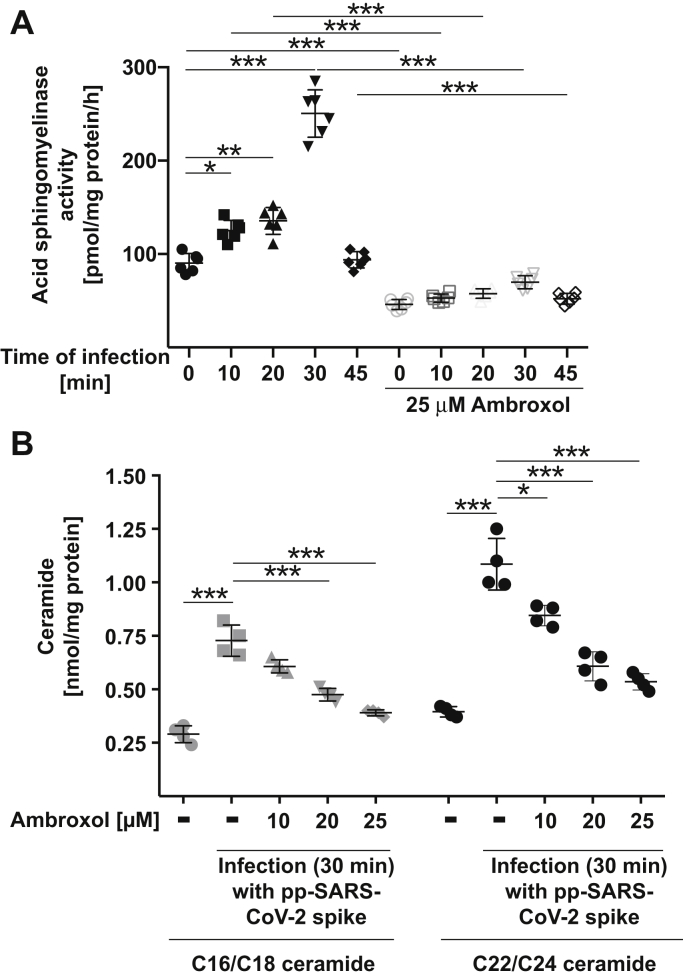
Figure 2.
Ambroxol prevents activation of the acid sphingomyelinase and release of ceramide upon infection with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike.A, Vero-E6 cells were preincubated with 25 μM ambroxol for 60 min or were left untreated. Cells were infected with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike for the indicated times or were left uninfected (0). Cells were lysed in 250 mM sodium acetate (pH 5.0) and 0.2% NP-40, and acid sphingomyelinase activity was determined by measuring the consumption of added [14C]sphingomyelin. Displayed are the means ± SD of the activity of the acid sphingomyelinase from six independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ANOVA followed by post hoc Student's t tests. Closed symbols give the time course without ambroxol, and open symbols give the time course with 25 μM ambroxol. B, cells were treated with 10, 20, or 25 μM ambroxol for 1 h and infected with pp-SARS-CoV-2 spike for 30 min or left untreated or uninfected, washed, and organically extracted to quantify C16/C18 ceramide and C22/C24 ceramide levels by using the ceramide kinase method. Displayed are the means ± SD of the ceramide concentrations from each six independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ANOVA, followed by post hoc Student's t tests, as indicated or compared with the corresponding value without inhibitor. Gray symbols represent 16/C18 ceramides, and black symbols represent C22/24 ceramides. NP-40, Nonidet P40; pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2, vesicular stomatitis virus pseudoviral particles presenting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on their surface.