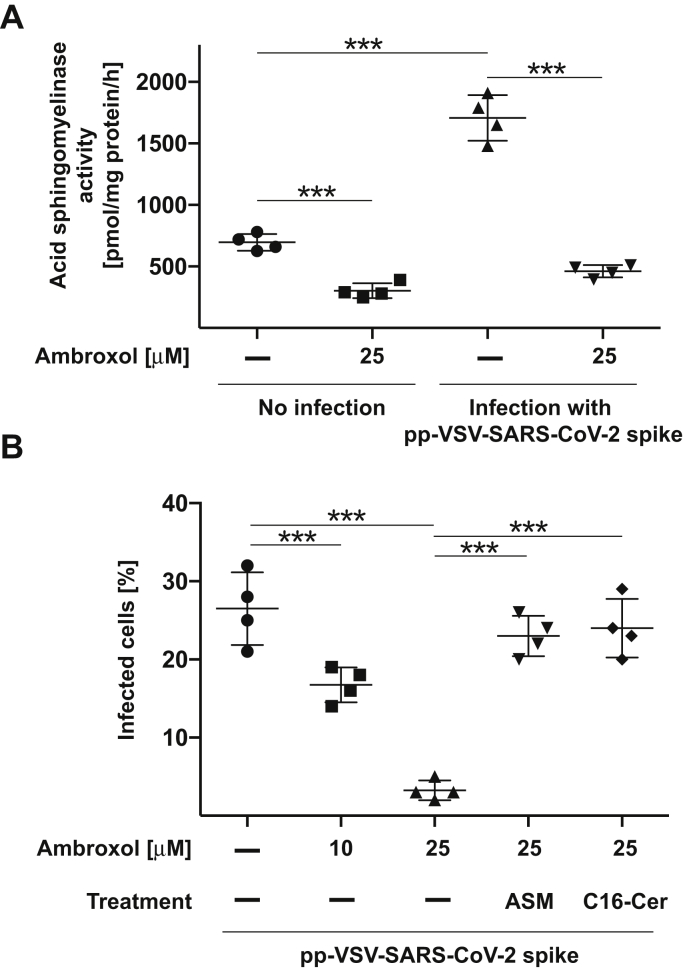
Figure 5.
Ambroxol prevents activation of the acid sphingomyelinase by an infection of freshly isolated human nasal epithelial cells with pp-VSV-SARS-Cov-2 spike in vitro.A, freshly isolated human nasal epithelial cells were incubated with 25 μM ambroxol for 1 h or left untreated and infected with pseudoviral particles of pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike for 30 min or left uninfected. The medium was removed, cells were lysed, and activity of the acid sphingomyelinase was determined by consumption of added [14C]sphingomyelin. Given are the means ± SD of the acid sphingomyelinase activity from four independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ANOVA, followed by post hoc Student's t tests. B, freshly isolated human nasal epithelial cells were incubated with 10 μM or 25 μM ambroxol for 1 h and infected with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike. Infection was determined by counting eGFP-positive cells in at least 500 cells/sample. Reconstitution of ceramide by application of 0.2 U/ml purified acid sphingomyelinase, or 10 μM C16 ceramide (C16-Cer) restored infection in human nasal epithelial cells treated with ambroxol. Given are the means ± SD of the percentage of eGFP-positive, that is, infected cells, from four independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ANOVA followed by post hoc Student's t tests. eGFP, enhanced GFP; pp-VSV-SARS-Cov-2, vesicular stomatitis virus pseudoviral particles presenting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein on their surface.