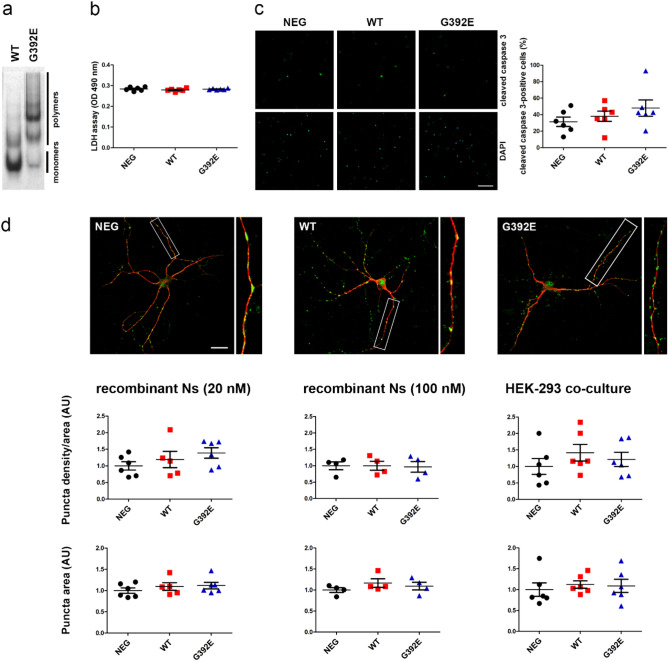
Figure 4.
Extracellular G392E-mutant neuroserpin polymers are not toxic on cultured neurons. Primary hippocampal neurons at DIV14 were treated for 18 h with human recombinant neuroserpin (wild-type or G392E-mutant) or solvent alone (NEG). Six independent neuronal preparations were treated (n = 6). (a) Non-denaturing PAGE followed by Coomassie staining of human recombinant wild-type and G392E-mutant neuroserpin. (b) Culture media were collected and analyzed for LDH activity (LDH assay). No differences between groups were detected (p = 0.4472). (c) Treated neurons were stained with an antibody against cleaved caspase 3. Pictures were taken from six fields for each condition. Quantification of positive cells as percentage of total DAPI-positive cells did not reveal increase in apoptosis upon treatment (p = 0.3146). (d) Representative immunocytochemical staining of treated neurons to reveal MAP2-positive dendrites (red fluorescence) and synaptophysin-positive synaptic puncta (green fluorescence). Neurons were treated either with human recombinant wild-type or G392E-mutant neuroserpin (20 or 100 nM) or by co-culturing them with HEK-293 cells overexpressing either wild-type or G392E-mutant neuroserpin. Pictures were taken from 10–12 neurons for each condition. Density of synaptic puncta as well as synaptic puncta area were quantified using the software SynPAnal, value for the negative control was set to 1 (AU, arbitrary units). No significant differences between groups were found (for p-values, s. Supplementary Table S1). Scale bars: 75 µm in (c), 25 µm in (d).