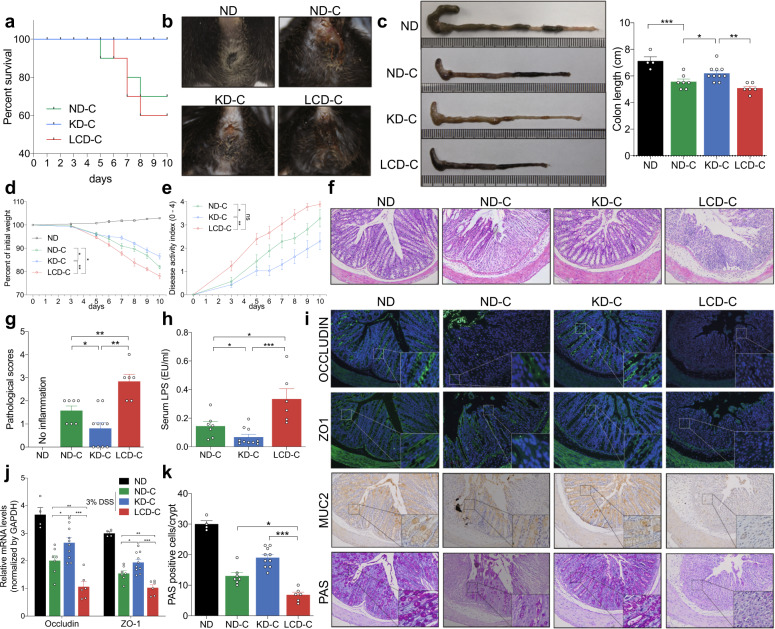
Fig. 3.
KD alleviates inflammatory responses and protects mucosal barrier function in mice with colitis. a Survival curves of mice with DSS-induced colitis fed with a KD, LCD, or ND. b Representative images of bloody diarrhea. c Representative images of the colon at 1.5 weeks after DSS induction. Colon length shown as a chart. d Body weight change in mice receiving 3% DSS in drinking water. e DAI in each group. f Representative colon H&E staining images (original ×magnification 200). g Changes in colonic section pathological scores. h Serum LPS levels detected by end-point chromogenic tachypleus amebocyte lysate. i Representative images of immunofluorescence, IHC and PAS staining in colon tissues with antibodies against Occludin, ZO-1, and MUC-2 (original magnification ×200). j Colon Occludin and ZO-1 mRNA expression measured by qRT-PCR. k Number of PAS-positive cells per villus/ crypt. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. (KD-C, n = 10; LCD-C, n = 6; ND-C, n = 7; ND, n = 4). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (c–e, g, h, j, k). KD ketogenic diet, LCD low-carbohydrate diet, ND normal diet, DSS dextran sulfate sodium, LPS lipopolysaccharide, IHC immunohistochemistry, PAS periodic acid schiff